
In recent times, the emergence of nitrosamine impurities in certain generic drug substances has prompted a re-evaluation of industry practices. This blog takes a deep dive into the multifaceted world of nitrosamine mitigation, specifically in the context of generic drug products. Moreover, it also throws light upon considerations made for Nitrosamine Drug Substance Related Impurities. We explore the intricacies of maintaining quality, ensuring bioequivalence, and understanding the pivotal role of regulatory experts in this critical process.
The Nitrosamine Challenge: A Regulatory Call-to-Action
Nitrosamines, a class of compounds known to be potential carcinogens, present a complex regulatory challenge. Regulatory agencies, including the U.S. FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), have responded with stringent limits and guidelines for the presence of these impurities in pharmaceutical products. This necessitates a comprehensive approach to understanding, detecting, and mitigating the risk of nitrosamine impurities in generic drug products.
Bioequivalence Challenges in Generic Products: Balancing Safety and Equivalence
Bioequivalence is the cornerstone of generic drug development, ensuring that a generic product is therapeutically equivalent to its reference counterpart. This critical aspect becomes even more intricate in the context of mitigating nitrosamine-related impurities.
1. Ensuring Consistency in Formulation
The presence of nitrosamine impurities hinges on the consistent delivery of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) to the patient. Regulatory experts, in collaboration with formulation scientists, play a pivotal role in ensuring that any adjustments made to mitigate impurities do not compromise the formulation's stability or efficacy.
2. Impacts on Absorption and Pharmacokinetics
Nitrosamine impurities can potentially affect the absorption and pharmacokinetics of the drug. This is particularly concerning in the context of generic products, where subtle variations can have pronounced effects. Regulatory experts guide these studies to ensure they adhere to regulatory standards and provide meaningful insights into the safety and efficacy of the generic product.
3. Dissolution Studies: A Key Component
Nitrosamine impurities can influence dissolution rates, and regulatory experts work closely with formulation and analytical teams to develop and implement robust dissolution testing methods. These methods must be sensitive enough to detect variations in dissolution profiles that may arise due to the presence of impurities.
4. Post-Approval Monitoring and Vigilance
Even after regulatory approval, the monitoring of generic products for the presence of nitrosamine impurities continues. Post-approval studies and pharmacovigilance efforts are spearheaded by regulatory experts who work collaboratively with manufacturers to implement robust monitoring programs. This ongoing vigilance is crucial to promptly identify and address any emerging safety concerns associated with nitrosamine impurities.
The Role of Regulatory Experts: Navigating the Complex Landscape
Regulatory affairs professionals play a pivotal role in mitigating the challenges posed by nitrosamine-related impurities in generic drug products. Their multifaceted responsibilities extend across various domains and are captured in the pie chart below:
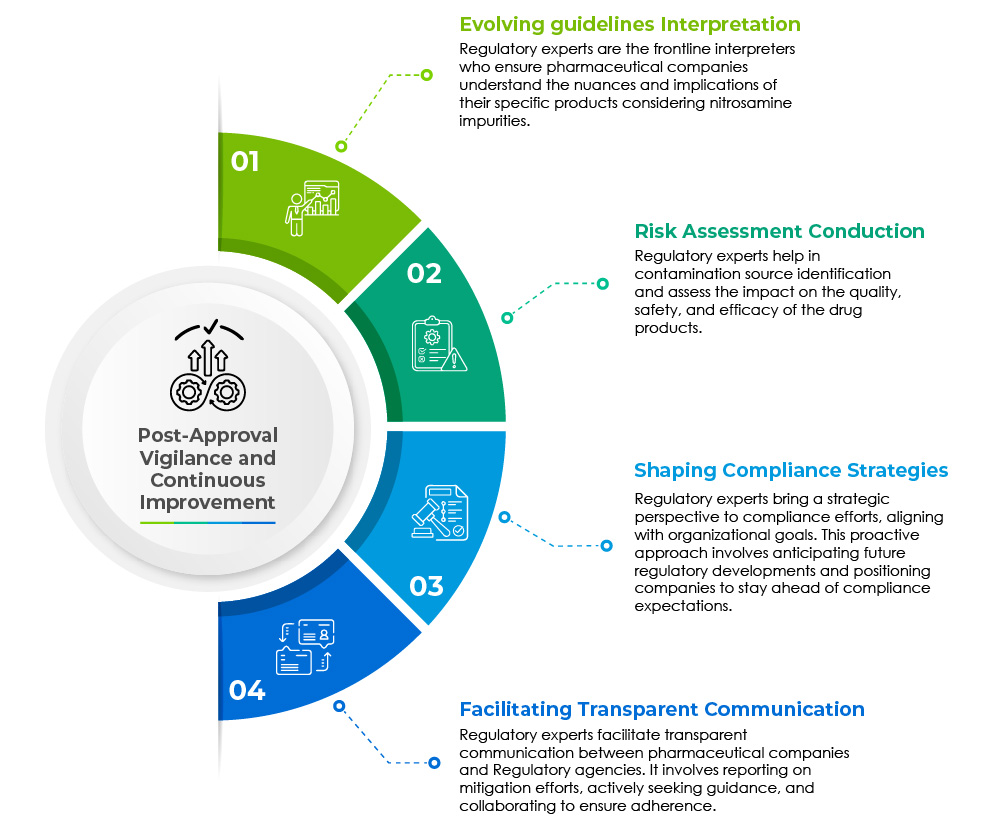
Post-approval vigilance and continuous improvement are the cornerstones for swift regulatory assistance.
Conclusion: Safeguarding Public Health Through Vigilance and Expertise
Mitigating nitrosamine-related impurities is not merely a regulatory requirement; it's a commitment to public health. As the pharmaceutical industry navigates this challenge, the role of regulatory experts becomes paramount. Their ability to merge compliance with innovation ensures that generic drug products not only meet regulatory standards but also contribute to a safer and healthier future. At Freyr, our regulatory experts leverage their expertise to gain a competitive advantage in such pursuits for pharma companies. Consult us to know more.









