SaMD Registration in the US – Overview
Answered on this page
- Is my software an SaMD?
- Which risk class of SaMD requires a 510(k)?
- SaMD registration and compliance – the 510(k) process
- How long is the clearance valid?
Is my software an SaMD?
According to International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF), SaMD is a:
- Software intended to be used for one or more medical purposes.
- Performs these purposes without being part of a hardware medical device.
Which risk class of SaMD requires a 510(k)?
Determining the SaMD classification for your software is an important step in the registration process. Once your software has been classified as SaMD, it becomes essential to understand the Regulatory pathway it requires for gaining market entry into the US. SaMD is typically categorized into different classes, based on their risk levels. Class II SaMD is considered moderate risk, requires a 510(k) clearance, and relies on proving substantial equivalence with the legally marketed predicate device. The clearance process ensures that your SaMD is substantially equivalent to existing devices, which helps guarantee its safety and efficacy before it is commercialized.
SaMD registration and compliance – the 510(k) process
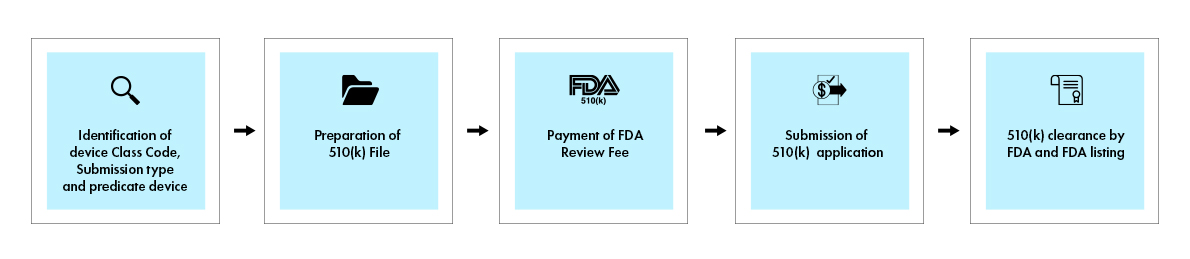
The 510(k) process involves a comprehensive submission that demonstrates substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device. When a decision is made, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issues a decision letter to the submitter via email. A 510(k) application that receives a substantial equivalence decision letter is deemed “cleared”. It is then listed in the 510(k) database, with the 510(k) summary attached. The figure below provides a visual overview of the key steps involved in the 510(k) process.
How long is the clearance valid?
A 510(k) clearance remains valid until there are significant changes made to the device or the applicable regulations. However, it is important to note that the US FDA can request periodic reports or additional information to ensure ongoing compliance and safety.
In conclusion, SaMD registration requires a thorough understanding of SaMD classification, SaMD compliance, and Regulatory processes. Seeking SaMD consulting services can provide expert guidance in navigating the complexities and ensuring a successful registration outcome.
SaMD Registration in the US
- Comprehensive US FDA Regulatory strategy for SaMD.
- SaMD classification.
- Predicate device identification.
- Establishing substantial equivalence with the predicate device.
- Gap analysis for US FDA compliance.
- Compilation of 510(k) technical file, according to the US FDA’s Premarket Submissions Guidance for Software.
- Creation of the eCopy/eSTAR template.
- Validation and submission of the eCopy/eSTAR template.
- Liaising services for device approval.
- Support for RTA response and AINN deficiencies.
- Consultation services for addressing deficiencies.
- Establishment registration with the US FDA.
- Device listing and FURLS database maintenance.
- Legal Representative (LR) services.

- Extensive experience with diverse 510(k) registrations.
- Expertise with 510(k) compilation, as per the US FDA’s Premarket Notification (510[k]) requirements.
- Additional support for handling 510(k) queries.
- On-time submission of deliverables.
- Up to date with the US FDA’s new amendments on SaMD.









