Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) Overview
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) is the latest booming topic in the healthcare segment. The SaMD market is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 10.78%, globally. This growth is triggered by various factors such as the adoption of Internet of Things (IoT), the digital healthcare platforms, and the adoption of software for continuous monitoring of physiological parameters by healthcare providers for remote assistance. However, this promising landscape also presents unique challenges, one of them being determining if it falls within the medical device category and adheres to the Regulatory requirements.
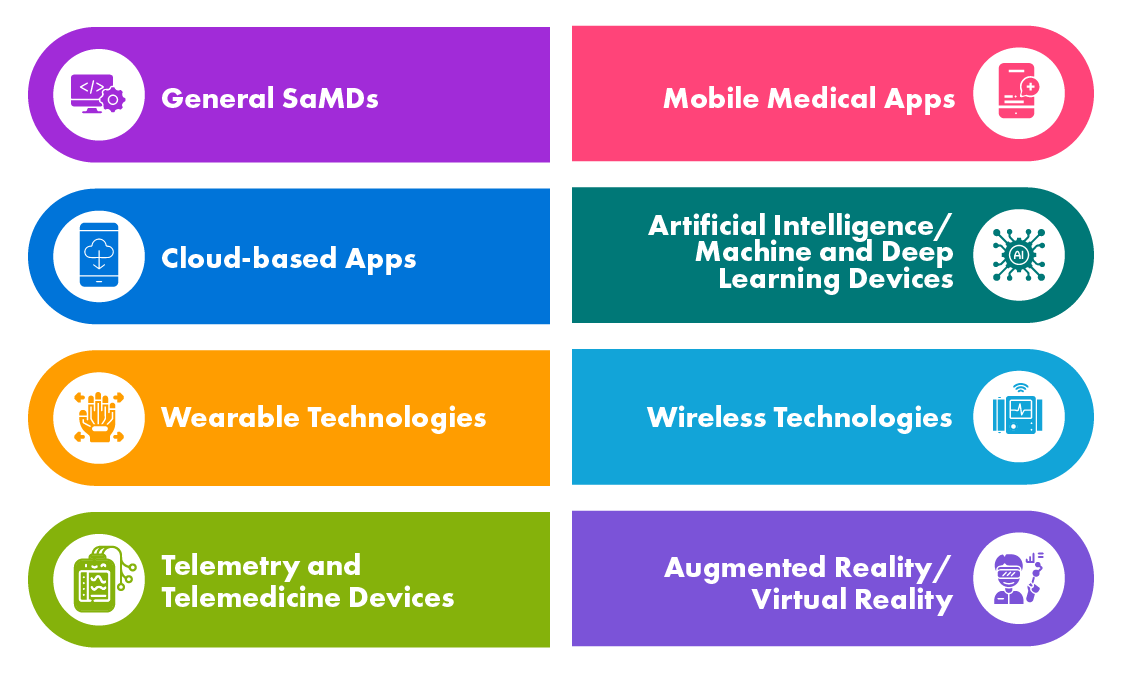
Different Types of Digital Health Products
Global Regulatory Scenario for Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) Registration
SaMDs are used in various applications such as screening and diagnosis, monitoring and alerting, disease management, etc. The Health Agencies of the developed countries such as the EU, the US, Canada, and Australia have defined regulations around SaMDs and some of them have already developed guidance documents while others are in the process.
Some regulated and non-regulated markets consider software as medical devices but do not have differentiated and specific guidelines for the Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) classification. They follow the internationally accepted harmonized guidelines for the evaluation and approval of the software.
Below listed are some of the prominent guidelines available on Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) Registration:
- IMDRF guidance for classification, Quality Management System (QMS), cybersecurity assessment, and clinical evaluation.
- The EU MDR 2017/745 has detailed out the regulatory requirements and guidance for this device category.
- The MDCG guidance on qualification and classification of SaMD, Clinical Evaluation Reports (CER)/Performance Evaluation Reports (PER) requirements for SaMD.
- The US FDA guidance on cybersecurity, clinical evaluation, and registration requirements for different types of software such as decision systems, Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), mobile applications, etc.
- Health Canada guidance document on SaMD definition and classification.
- TGA’s new regulations for software-based medical devices.
The registration of SaMD in other global markets shall be handled in a case-by-case approach and requires close interaction with the respective Health Agency for approval. The general pathway followed for registration of SaMD includes:
- Determining whether a given software qualifies as a SaMD.
- Classification of the devices based on the risk involved.
- Identify applicable standards and data requirements by the concerned Health Agency.
- Generate data as required by the respective Agency.
- Compilation of technical file as per the country’s requirement.
- Submission and query resolution till approval.
- Post-approval life cycle management.
Our Competencies
- Regulatory Intelligence Services (Market + Labeling Support related)
- Regulatory Due Diligence / Strategy Reports
- Qualification and Classification of SaMD
- Product Classification Application to NB
- Gap Analysis
- Pre-Submission meetings with FDA
- Identification of Applicable Standards
- Risk Management Activities
- Risk Management Support
- Labeling Support
- Creation/review/update of SaMD Specific procedues/templates
- UDI/ GUDID
- Product registration (Software registration)
- Establishment Registration
- Device Listing
- HA Query response—SaMD services
Why Freyr?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Medical software regulation is overseen by various global Regulatory Bodies, including the FDA in the United States, the EMA in Europe, and the PMDA in Japan. These Agencies classify medical software based on the risk and establish guidelines for safety, quality, and effectiveness. Compliance with the ISO standards, such as ISO 13485 and 62304 is required.
Determining the risk classification of Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) involves assessing factors such as intended use and potential harm. SaMDs are classified like traditional medical device based on the importance of the information provided to healthcare decision and the state of healthcare situation or condition as non-serious, serious, and critical. Regulatory guidelines and expert consultation are crucial in this process, ensuring compliance and patient safety.
SaMD refers to software that is intended to be used for one or more medical purposes, without being part of a physical medical device. It operates on general-purpose computing platforms like smartphones, tablets, or personal computers. On the other hand, SiMD is a software that is an integral component of a physical medical device, contributing to its functionality and performance. SiMD cannot be used independently and relies on the associated medical device to perform its intended purpose.
A software that is embedded as part of a hardware medical device and is necessary to drive the intended medical purpose IS NOT considered as a SaMD.
The timeline for achieving SaMD compliance is influenced by the risk class and Regulatory requirement. But, with the right Regulatory assistance you can ensure smoother compliance process with minimum risks.
Medical Device Registration
- Comprehensive Regulatory strategy for SaMDs.
- Regulatory and market intelligence support.
- Product classification and registration services for SaMDs.
- Regulatory support for SaMD product development documents.
- Consultation services on SaMD clinical evaluation studies.
- Post-approval change management.
- Local representation service.

- Comprehensive Regulatory strategy for SaMDs.
- Regulatory and market intelligence support.
- Product classification and registration services for SaMDs.
- Regulatory support for SaMD product development documents.
- Consultation services on SaMD clinical evaluation studies.
- Post-approval change management.
- Local representation service.