Pharma Compliance Audit, and Validation Services
Harness a decade of proficiency with our services through compliance assessments, meticulous audits, and robust validation processes.
Browse Topics
- What is pharma Compliance, Audit, and Validation?
- What is the importance of Compliance, Audit and Validation in the pharma industry?
- Major challenges in the Compliance, Audit and Validation space
- What are GxP Audits?
- Understanding Remote Audits
- What is Computer System Validation (CSV), and why is it crucial in the pharmaceutical industry?
- How does CSV differ from Computer System Assurance (CSA)
- What are the components of a CSA program?
- How does CSA contribute to data integrity in the pharmaceutical industry?
- What role does Regulatory compliance play in CSA?
- How does a strategic Regulatory compliance partner help?
- Why choose Freyr?
- Our Services
What is pharma Compliance, Audit, and Validation?
Last updated on: Sepetember, 2024
In the pharmaceutical realm, compliance, audit, and validation processes are integral, safeguarding adherence to Regulatory standards, data integrity, and the production of safe, effective products. Compliance entails aligning operations with industry regulations and internal policies. Audits, systematic reviews, verify compliance, identify improvement areas, and mitigate risks. Validation guarantees that systems, processes, and equipment consistently meet predefined requirements.
Companies seek expert guidance to navigate seamlessly. Industry leaders adeptly manage these processes, ensuring global standards without compromising product efficacy or safety. As the pharmaceutical sector evolves, strategic compliance, audit, and validation approaches become instrumental for sustained success. By upholding these processes, companies meet Regulatory benchmarks and foster a culture of excellence and innovation in a dynamic and challenging industry.
Collaborate with a trusted partner for strategic guidance and tailored solutions that empower your pharmaceutical operations to thrive in a dynamic Regulatory landscape.

What is the importance of Compliance, Audit and Validation in the pharma industry?
Compliance, audit, and validation are critical components in the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring that products are safe, effective, and produced according to Regulatory standards.
- Ensures Product Safety and Efficacy: Compliance with regulations ensures that pharmaceutical products meet stringent safety and efficacy standards before reaching the market. This involves rigorous testing and validation processes to confirm that products perform as intended and do not pose risks to patients.
- Maintains Regulatory Adherence: Regular audits and validation help companies adhere to complex and evolving regulations set by health authorities. This includes compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), Good Clinical Practice (GCP), and other industry standards, reducing the risk of Regulatory penalties and product recalls.
- Enhances Quality Assurance: Validation processes, including equipment and system validations, ensure that manufacturing and testing processes consistently produce high-quality products. Audits verify that these processes are followed correctly, leading to improved product quality and reliability.
- Supports Market Access and Reputation: Effective compliance and validation practices support market access by demonstrating adherence to Regulatory requirements. This enhances the company’s reputation and credibility, building trust with healthcare professionals, patients, and Regulatory bodies.
- Facilitates Continuous Improvement: Audits provide insights into process efficiencies and areas for improvement, leading to better quality control and operational practices. This ongoing assessment and adjustment help in maintaining high standards and adapting to changes in regulations and industry best practices.
Major challenges in the Compliance, Audit and Validation space
The Compliance, Audit, and Validation space faces several major challenges that can impact pharmaceutical companies' ability to meet Regulatory requirements and maintain high standards of quality and safety:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Pharmaceutical companies must adhere to stringent regulations from agencies like the FDA and EMA, which require rigorous documentation and quality control measures. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including fines and product recalls. |
| Access Control and Security | Ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive areas and information is critical. This involves implementing advanced access control systems and maintaining cybersecurity against threats, which can be complex and costly. |
| Computer System Validation (CSV) | Validating computer systems used in GxP environments is essential but often burdensome and poorly defined. The process requires significant time and resources, especially when a standard approach is applied indiscriminately. |
| Employee Training and Awareness | Continuous training programs are necessary to ensure that employees understand compliance protocols and their importance. Inadequate training can lead to non-compliance and errors in processes. |
| Documentation and Record-Keeping | Maintaining accurate and comprehensive documentation is vital for compliance. Inadequate documentation is a common issue that can lead to Regulatory observations and failures during audits. |
| Data Integrity | Ensuring the integrity and accuracy of data is crucial, especially in managing large volumes of information. Challenges include manual data handling and the need for robust data management systems. |
| Vendor Management | Reliance on third-party vendors for software and services necessitates thorough validation and compliance checks. Managing these relationships and ensuring they meet Regulatory standards can be challenging. |
| Technological Complexity | The increasing complexity of technologies, including AI and cloud-based systems, presents new validation challenges and requires ongoing adaptation to evolving Regulatory landscapes. |
| Inadequate Quality Control | Many pharmaceutical companies struggle with maintaining high-quality standards across processes, which can lead to contamination, cross-contamination, and other quality issues. |
| Continuous Improvement and Monitoring | Regular audits and inspections are essential for identifying weaknesses in compliance systems. However, many organizations fail to implement proactive measures for continuous improvement |
- Evolving Regulations: Keeping up with rapidly changing regulations and guidelines across different regions can be challenging. Pharmaceutical companies must continuously update their compliance practices to adhere to new or revised Regulatory standards, which can require significant resources and adjustments.
- Complexity of Global Standards: Navigating the diverse and complex Regulatory requirements of different countries and regions adds to the challenge. Each jurisdiction may have its own set of rules and standards, making it difficult to achieve consistent compliance across global markets.
- Data Integrity and Security: Ensuring the integrity and security of data throughout the compliance, audit, and validation processes is critical. Companies must implement robust systems and controls to protect against data breaches, tampering, or inaccuracies, which can have severe consequences for product approval and patient safety.
- Resource Constraints: Limited resources, including time, personnel, and budget, can hinder the effectiveness of compliance and audit activities. Companies often struggle to balance the demands of maintaining compliance with the need to allocate resources for other critical business functions.
- Managing Documentation and Record-Keeping: Proper documentation and record-keeping are essential for demonstrating compliance and conducting effective audits. However, managing vast amounts of documentation, ensuring its accuracy, and maintaining accessibility can be challenging, especially in a highly regulated environment.
- Integration of New Technologies: Incorporating innovative technologies into existing compliance and validation processes can be complex. While technologies like automation and AI (Artificial Intelligence) offer significant benefits, their integration must be carefully managed to ensure they comply with Regulatory requirements and do not introduce new risks.
- Training and Competency: Ensuring that staff are adequately trained and competent in compliance, audit, and validation processes is crucial. Ongoing training programs are necessary to keep personnel updated on Regulatory changes and best practices, which can be resource intensive.
- Addressing Audit Findings: Effectively addressing and correcting issues identified during audits can be challenging. Companies must implement corrective and preventive actions promptly while ensuring that these actions do not disrupt ongoing operations or affect product quality.
- Balancing Compliance with Innovation: Striking a balance between complying with stringent regulations and pursuing innovation can be difficult. Companies must navigate the Regulatory landscape while continuing to develop and introduce new products and technologies.
- Ensuring Consistency Across Operations: Maintaining consistency in compliance practices and validation processes across different departments, facilities, and stages of the product lifecycle is essential but challenging. Variability in practices can lead to non-compliance and quality issues.
What are GxP Audits?
What is a GxP independent compliance audit and who performs it?
A GxP compliance audit is a process developed to ensure that companies adhere to preset standards of quality, safety, and Regulatory compliance. It can cover various aspects of pharmaceutical products and processes, such as Good Laboratory Practice (GLP), Good Clinical Practice (GCP), Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), and Good Pharmacovigilance Practice (GVP).
The audit evaluates the level of compliance with the applicable laws, regulations, guidelines, and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and identifies the gaps, risks, and opportunities for improvement. The audit also provides recommendations and corrective actions to address the findings and enhance the quality systems.
The benefits of a GxP audit include:
- Providing an unbiased and objective assessment of the quality systems and compliance level.
- Enhancing the confidence and trust of the regulators, customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders.
- Reducing the likelihood and severity of Regulatory inspections, observations, and sanctions.
- Improving the quality, safety, and efficacy of the products and processes.
- Increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of the operations and reducing the costs and errors.
- Supporting the continuous improvement and innovation of the products and processes.
A GxP audit is performed by a qualified and experienced auditor or a team of auditors with relevant knowledge, skills, and credentials in the pharmaceutical industry and the specific GxP area. The auditor or the audit team should be independent of the company being audited and follow the professional standards and ethical principles of auditing. They should also use appropriate tools and methods to conduct the audit, such as checklists, interviews, observations, document reviews, sampling, testing, etc. Freyr offers end-to-end support in GxP audits. As an industry leader, our experts will make your compliance journey seamless.
Regulatory Framework for GxP Audits
GxP compliance is a set of regulations that govern various regulated industries, including pharmaceuticals, medical devices, food, beverages, and biotechnology. The primary goal of GxP compliance is to maintain product quality and ensure public safety. Here are some key points:
- GxP Compliance Overview:
- GxP encompasses several standards, including Good Laboratory Practice (GLP), Good Clinical Practice (GCP), Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), and Good Pharmacovigilance Practice (GVP).
- These standards ensure that products are thoroughly tested, manufactured, and handled throughout their lifecycle.
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH):
- The ICH provides guidelines for GxP compliance.
- The ICH Q7A Good Manufacturing Practice Guidance specifically addresses manufacturing practices for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
- FDA Inspections:
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) conducts inspections to assess compliance with GxP regulations.
- These inspections evaluate adherence to specific FDA regulations and guidelines.
- Health Canada Inspections:
- Health Canada, the Regulatory authority in Canada, also conducts inspections to ensure GxP compliance.
- These inspections focus on various aspects, including manufacturing, quality control, and distribution.
- Assessment Criteria for GxP Audits:
Compliance in GxP independent audits is typically assessed against a range of criteria, which may include:
- Regulatory Requirements: Compliance with specific regulations, guidelines, and laws applicable to the GxP area (e.g., FDA regulations, ICH guidelines, or ISO standards).
- Quality Systems: Evaluation of quality management systems, documentation practices, and record-keeping.
- Process Validation: Verification that processes are validated and meet predefined criteria.
- Training and Competency: Assessment of personnel training and qualifications.
- Risk Management: Identification and mitigation of risks related to product quality and safety.
Learn how a proven Regulatory expert can help you create the ideal GxP audit framework suited to your needs and help you stay compliant with global regulations.
Benefits of Conducting GxP Compliance Audits
GxP audits have numerous benefits for any organization. Firstly, they provide an impartial and independent assessment of risk and compliance within the organization, allowing companies to identify areas of non-compliance or potential risk that might be overlooked from internal audits. These audits are essential for ensuring that companies adhere to certain standards of quality, safety, and Regulatory compliance.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive Review | Thorough assessment by a qualified third party to identify non-compliance areas. |
| Regulatory Standards | Adherence to GxP (good practices) standards like GMP, GCP, and GLP. |
| Tailored Scope | Customized audit scope based on specific products and processes. |
| Qualified Auditors | Experienced auditors familiar with regulations. |
| Regulatory Framework | Follows ICH Q7A, FDA, and Health Canada guidelines. |
| Benefits | Impartial assessments, risk prevention, quality maintenance, and scalability. |
Here are some key points about GxP compliance audits:
- Comprehensive Review: GxP audits involve a thorough review process conducted by a qualified third-party organization or consultant. The purpose is to identify any areas of non-compliance within the organization and provide recommendations for improvement.
- Regulatory Standards: The regulations reviewed during these audits are defined by GxP (good practices) standards, such as Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), Good Clinical Practices (GCP), and Good Laboratory Practices (GLP). These standards ensure that products, services, and processes consistently meet relevant Regulatory requirements.
- Tailored Scope: An independent audit's scope is customized to the specific products and processes of the organization. It may include personnel management, facility management, record keeping, quality assurance and control, product and process design, and technical operations.
- Qualified Auditors: The audit must be conducted by a qualified and experienced auditor who is familiar with applicable regulations and has the necessary expertise to assess the organization’s procedures and processes effectively.
- Regulatory Framework: GxP audits follow frameworks such as the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) Q7A Good Manufacturing Practice Guidance, FDA inspections, and Health Canada Inspections. These frameworks provide guidance on basic requirements for production, quality assurance, distribution, and other critical activities related to safe product manufacture.
- Benefits: GxP audits offer impartial assessments, help prevent non-compliance issues, maintain quality standards, and ensure accountability. Outsourcing these audits provides access to expertise, objectivity, cost efficiency, and scalability while allowing companies to focus on core competencies.
If you’re looking for GxP compliance solutions, consider Freyr. We specialize in Regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and safety across the life sciences industry. With our expertise, you can ensure adherence to GxP standards, streamline processes, and maintain high-quality products and services.
Tips to Prepare Your Organization for an Audit
Preparing your organization for an audit is a strategic process that involves meticulous planning and a proactive approach. Firstly, ensure that all records, documentation, and relevant files are organized and readily accessible. A well-organized filing system facilitates a smoother audit process and reflects positively on your organization's professionalism.
Secondly, conduct an internal pre-audit to identify potential areas of concern. This self-assessment allows you to address any issues or discrepancies before the external audit. By proactively resolving issues, you demonstrate your commitment to compliance and transparency.
Thirdly, communicate and collaborate effectively with the audit team. Provide the necessary information, access to relevant personnel, and a conducive working environment. Clear communication helps build a positive rapport with auditors, fostering a collaborative atmosphere during the audit process.
Lastly, ensure your team is well-trained and aware of the audit process. Educate employees on their roles, responsibilities, and the importance of compliance. By instilling a culture of preparedness and cooperation, your organization can navigate audits with confidence and professionalism.
Understanding Remote Audits
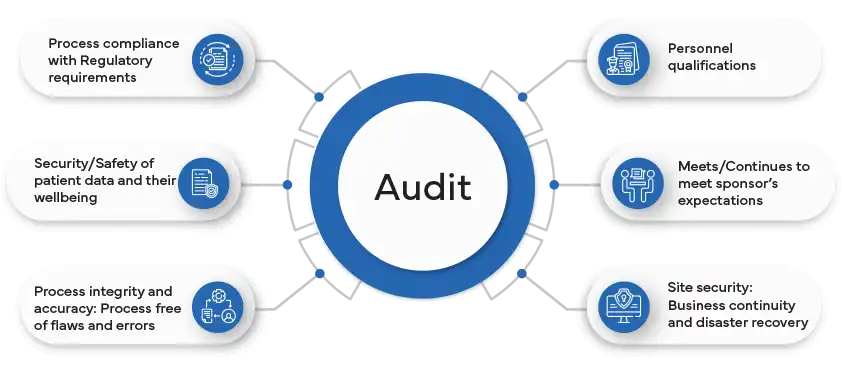
What is a remote audit in the pharmaceutical industry, and how does it differ from traditional onsite audits?
A remote audit in the pharmaceutical industry is a comprehensive evaluation of a company's processes, facilities, and systems conducted by Regulatory authorities or auditors without a physical on-site presence. This audit is facilitated through digital communication tools, collaborative software, and remote access to relevant documents and systems. It aims to ensure compliance with Regulatory standards, assess quality management systems, and verify adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), Good Clinical Practice (GCP), or other applicable regulations.
The difference between remote and traditional onsite audits is the absence of physical presence during a remote audit. Instead of visiting the company's premises, auditors rely on virtual interactions, electronic documentation, and remote access to systems. This approach offers flexibility and efficiency, allowing audits to take place regardless of geographical distances and travel restrictions. However, challenges such as limited direct observation of facilities and potential cybersecurity concerns need to be addressed to ensure the effectiveness of remote audits.
Despite the differences, the objectives of both remote and traditional audits remain the same – to verify compliance, identify areas for improvement, and ensure the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products. The choice between remote and onsite audits depends on factors such as the nature of the audit, Regulatory requirements, and the company's capabilities in facilitating a thorough assessment through remote means.
Freyr leverages a decade of expertise to provide unparalleled Regulatory solutions, ensuring compliance and success in the dynamic pharmaceutical landscape.
Explore Regulatory excellence with us – your strategic partner for compliance success in the ever-evolving pharmaceutical industry. Connect with us to navigate Regulatory complexities seamlessly.
What challenges may arise during remote audits, and how are they addressed to ensure thorough assessments?
During remote audits, several challenges may arise, but organizations can take steps to address them and ensure thorough assessments. Here are some key challenges and their potential solutions:
- Building Key Relationships with Audit Stakeholders:
- Challenge: Remote work can hinder the development of strong relationships with audit stakeholders.
- Solution: Regular virtual meetings, open communication, and active engagement can help build and maintain relationships. Use video calls to establish a personal connection.
- Investing in Technology for Virtual Work:
- Challenge: Remote audits rely heavily on technology, and inadequate tools can hinder efficiency.
- Solution: Invest in robust audit management software, secure communication platforms, and collaboration tools. Ensure auditors have the necessary hardware and software.
- Developing Employees and Promoting a Positive Culture Remotely:
- Challenge: Remote work can lead to isolation and hinder professional growth.
- Solution: Provide virtual training, mentorship, and opportunities for skill development. Foster a positive culture through team-building activities, recognition, and regular check-ins.
- Cultivating an Intentional and Adaptive Mindset:
- Challenge: Remote auditors must adapt to changing circumstances and stay focused.
- Solution: Encourage flexibility, adaptability, and a growth mindset. Train auditors to handle unexpected situations and adjust their approach as needed.
Freyr is a trusted partner in Regulatory compliance and safety solutions for the life sciences industry. With deep domain expertise, innovative technology, and a global footprint, Freyr empowers organizations to navigate complex Regulatory landscapes seamlessly. Explore our services and contact us today to elevate your compliance journey.
How is Freyr better placed to help you with your remote audits?
Freyr, with its decade-long expertise, excels in facilitating seamless remote audits for the pharmaceutical industry. Leveraging advanced technologies and a deep understanding of Regulatory requirements, Freyr ensures a thorough and efficient audit process, addressing challenges such as limited physical presence and cybersecurity concerns.
Our dedicated team of Regulatory experts is adept at utilizing innovative digital solutions, ensuring a comprehensive virtual assessment of your processes, facilities, and documentation. Our proven record of accomplishment in remote audits reflects our commitment to delivering reliable and effective Regulatory solutions tailored to the evolving needs of the pharmaceutical landscape. With Freyr, you gain a trusted partner who understands the intricacies of remote audits and brings a proactive and collaborative approach to enhance your compliance journey.
What is Computer System Validation (CSV), and why is it crucial in the pharmaceutical industry?
Computer System Validation (CSV) is a critical process in the pharmaceutical industry that ensures the integrity, reliability, and compliance of computerized systems used for various purposes. Let’s delve into the details:
- Definition and Purpose:
- CSV is the documented process that assures a computer-based system will produce information or data meeting predefined requirements.
- Its primary purpose is to validate and verify that computer systems consistently perform as intended, maintaining data accuracy, reliability, and security.
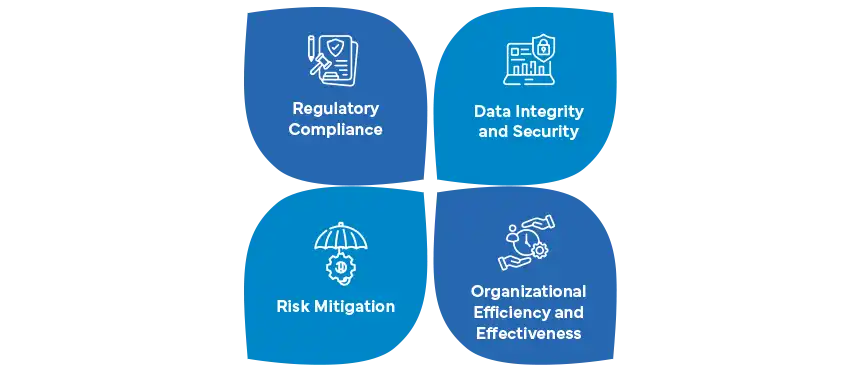
- Importance in Pharma:
- Regulatory Compliance: The pharmaceutical industry operates under strict regulations (such as Good Manufacturing Practice or GMP) to ensure product quality, safety, and efficacy.
- Data Integrity: Accurate and reliable data are crucial for drug development, clinical trials, manufacturing, and distribution.
- Risk Mitigation: CSV helps identify and mitigate risks associated with computer systems, preventing errors, data loss, and non-compliance.
- Patient Safety: Properly validated systems contribute to the safety of patients by ensuring consistent quality and adherence to standards.
- Key Aspects of CSV:
- Requirements Definition: Clearly define system requirements, functionalities, and user expectations.
- Design and Configuration: Develop and configure the system according to specifications.
- Testing and Qualification: Rigorous testing (including unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing) to verify system performance.
- Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation throughout the system lifecycle.
- Change Control: Manage changes to the system, ensuring they don’t compromise its integrity.
- Challenges Addressed by CSV:
- Data Integrity: Prevent unauthorized access, data corruption, or manipulation.
- System Security: Protect against cyber threats and unauthorized modifications.
- Audit Trail: Maintain an indelible electronic data trail for Regulatory audits.
- Validation Maintenance: Regularly review and update validation to adapt to system changes.
How does CSV differ from Computer System Assurance (CSA)?
Computer System Validation (CSV) and Computer System Assurance (CSA) represent distinct approaches to ensuring the integrity and compliance of computerized systems in the pharmaceutical industry. CSV, a longstanding practice, primarily focuses on the validation phase of a system's lifecycle, ensuring that software systems meet Regulatory requirements through predefined protocols. On the other hand, CSA takes a more expansive and dynamic approach, covering the entire lifecycle of a computerized system, from development and implementation to operational use and eventual retirement.
CSV addresses the need for rigorous validation processes, emphasizing risk-based approaches to identify and mitigate potential issues. However, the pharmaceutical landscape is evolving, prompting the emergence of CSA as a more comprehensive strategy. CSA extends its focus beyond validation by adapting agile methodologies and incorporating continuous monitoring throughout a system's lifecycle. This holistic perspective allows organizations to proactively manage risks, especially in cybersecurity and data integrity, aligning with the industry's growing emphasis on technology and data security.
The adaptability of CSA is valuable in a rapidly changing Regulatory environment. While CSV adheres to traditional validation practices, CSA aligns with the evolving expectations of Regulatory authorities. It goes beyond periodic revalidation efforts, incorporating continuous monitoring, real-time data analytics, and proactive risk management strategies to ensure ongoing compliance and optimal performance. As the pharmaceutical industry embraces digital transformation, understanding the nuances between CSV and CSA becomes imperative for companies aiming to stay ahead in Regulatory compliance and system integrity.
In this context, Freyr, with its extensive experience and expertise, is well-equipped to guide pharmaceutical companies through the intricacies of both CSV and CSA, offering tailored solutions to meet the evolving demands of Regulatory compliance and technological advancements.
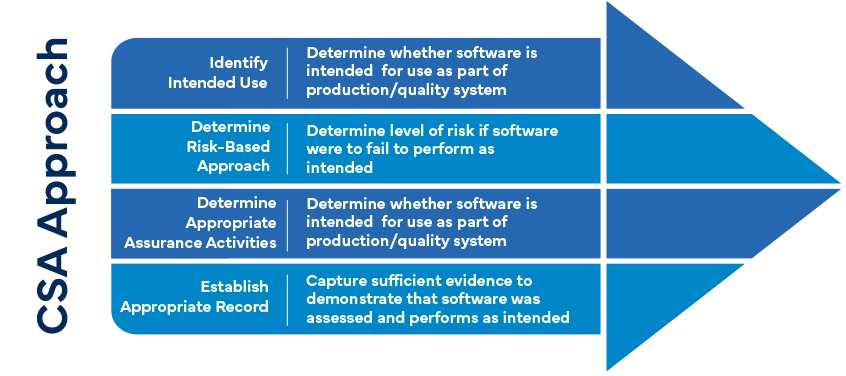
What are the components of a CSA program?
Computer Software Assurance (CSA) is a modern approach that enhances reliability, security, and compliance in computerized systems. Let’s explore its components and long-term benefits:
- Risk-based Approach:
- Component: CSA focuses on risk assessment and management.
- Importance: Identifying critical areas helps allocate validation efforts effectively.
- Unscripted Testing:
- Component: CSA includes unscripted testing beyond traditional scripted test cases.
- Importance: Unscripted testing mimics real-world scenarios, uncovering hidden issues.
- Continuous Performance Monitoring:
- Component: CSA involves ongoing monitoring of system performance.
- Importance: Detecting anomalies early prevents system failures and data integrity issues.
- Data Oversight:
- Component: CSA emphasizes data quality and integrity.
- Importance: Ensures accurate data for decision-making and compliance.
- External Validation Activities:
- Component: CSA collaborates with software suppliers for external validation.
- Importance: Independent validation adds confidence and reduces bias.
- Transition from CSV to CSA:
- Initial Steps:
- Understand CSA principles.
- Assess existing systems for risk.
- Prioritize critical functionalities.
- Benefits:
- Reduced validation workload.
- Agile response to changes.
- Enhanced system reliability.
- Initial Steps:
- Long-term System Reliability:
- CSA ensures:
- Adaptability: Systems evolve without compromising reliability.
- Security: Protection against cyber threats.
- Compliance: Continuous alignment with regulations.
- Quality: Consistent data and product quality.
- CSA ensures:
How does CSA contribute to data integrity in the pharmaceutical industry?
CSA upholds data integrity within the pharmaceutical industry by ensuring accuracy, consistency, and data reliability throughout a system's lifecycle. Unlike traditional approaches, CSA embraces a holistic strategy that extends beyond validation, actively addressing potential challenges and discrepancies that may arise over time.
One contribution of CSA to data integrity lies in its continuous monitoring capabilities. Rather than relying solely on periodic validation efforts, CSA involves real-time data analytics and proactive risk management measures. This approach enables organizations to detect and address potential data discrepancies, preventing inaccuracies from accumulating over time. CSA's emphasis on a dynamic and adaptive lifecycle model ensures that data integrity remains a constant focus, aligning with Regulatory expectations.
To prevent data discrepancies over time, CSA incorporates several strategic measures. Firstly, it employs robust change control processes, meticulously documenting any modifications to computerized systems or processes that could impact data integrity. Regular system audits and assessments are conducted to identify and rectify potential issues before they escalate. Also, CSA emphasizes the importance of user training and awareness programs to ensure that personnel understand the significance of maintaining data integrity and adhere to best practices.
In conclusion, CSA's proactive and comprehensive approach to data integrity sets it apart as a strategic solution in the pharmaceutical industry. By incorporating continuous monitoring, risk management, and stringent change control measures, CSA maintains data integrity and ensures that pharmaceutical companies are well-prepared to navigate the evolving landscape of Regulatory expectations. As organizations strive to uphold the highest standards in data integrity, CSA emerges as a key ally in their journey, aligning with industry trends and Regulatory advancements.
For organizations seeking guidance on implementing effective CSA strategies, Freyr is a reliable partner offering tailored solutions to address the unique challenges of the pharmaceutical landscape.
What role does Regulatory compliance play in CSA?
Regulatory compliance is a cornerstone of CSA, ensuring pharmaceutical companies adhere to evolving standards and guidelines throughout a system's lifecycle. Unlike the traditional focus of Computer System Validation (CSV), CSA emphasizes continuous compliance and adaptability to changing Regulatory landscapes. As companies transition from CSV to CSA, staying updated on evolving regulations becomes paramount.
In the context of CSA, Regulatory compliance involves aligning computerized systems with global and local Regulatory requirements from development through operational use and eventual retirement. CSA emphasizes ongoing compliance rather than periodic validation, fostering a proactive approach to address potential Regulatory changes promptly. This strategic alignment ensures that pharmaceutical companies are well-prepared to meet Regulatory expectations, safeguarding data integrity, patient safety, and overall system reliability.
Regular engagement with Regulatory authorities, participation in industry forums, and subscription to Regulatory publications provide valuable insights into evolving standards. Leveraging the expertise of Regulatory consultants and investing in continuous training for personnel involved in CSA processes further enhances Regulatory awareness. Collaborating with Regulatory partners, such as Freyr Solutions, offers a proactive approach, ensuring access to up-to-date Regulatory intelligence and tailored solutions to seamlessly navigate the transition.
Regulatory compliance in CSA is a dynamic and ongoing commitment that aligns with the industry's shift towards adaptability and continuous improvement. Staying informed, proactive, and partnering with Regulatory experts are crucial for companies transitioning from CSV to CSA, facilitating a smooth and compliant evolution in the ever-changing pharmaceutical landscape.
As a trusted Regulatory partner, Freyr provides the necessary support and expertise to guide companies through this transition, ensuring Regulatory excellence and compliance in the era of CSA.
How does a strategic Regulatory compliance partner help?
A strategic Regulatory compliance partner plays a critical role in ensuring that pharmaceutical companies meet Regulatory requirements and maintain high standards of quality. Here’s how they can help:
- Expert Guidance: A strategic partner provides expert advice on navigating complex and evolving regulations across different regions. They offer insights into the latest Regulatory changes, helping companies adjust their practices and maintain compliance.
- Streamlined Processes: They help streamline compliance processes by implementing best practices and efficient workflows. This includes developing robust systems for documentation, auditing, and validation, reducing administrative burdens, and improving overall efficiency.
- Risk Mitigation: By identifying potential compliance risks and vulnerabilities, a strategic partner helps mitigate risks before they become issues. They conduct thorough audits and assessments to ensure that all processes are compliant and address any gaps proactively.
- Training and Support: They offer training and support to ensure that staff are well-informed about Regulatory requirements and best practices. This helps build internal competency and ensures that everyone involved in compliance activities is up to date with current standards.
- Technology Integration: A strategic partner assists with the integration of innovative technologies, such as automation and AI, into compliance processes. They ensure that these technologies are implemented effectively and in accordance with Regulatory requirements, enhancing data integrity and process efficiency.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: They manage the creation, organization, and maintenance of crucial compliance documentation. This ensures that all records are accurate, complete, and readily accessible for audits and inspections.
- Regulatory Submissions and Approvals: They handle the preparation and submission of Regulatory documents and applications. This includes ensuring that submissions meet all necessary requirements and managing communications with Regulatory authorities to facilitate timely approvals.
- Corrective and Preventive Actions: A strategic partner supports the development and implementation of corrective and preventive actions in response to audit findings or compliance issues. They help ensure that these actions are effective and do not disrupt ongoing operations.
- Global Compliance Strategy: They develop and implement strategies for achieving global compliance, addressing the diverse Regulatory requirements of different markets. This ensures that products meet all necessary standards for international distribution and use.
- Ongoing Monitoring: They provide ongoing monitoring and support to keep companies informed of any Regulatory updates or changes. This proactive approach helps companies stay compliant and adapt to new regulations as they arise.
Why choose Freyr?
Over ten years in Regulatory compliance excellence.
Full spectrum of compliance, audit, and validation.
Expertise across diverse industries and geographies.
Utilizes innovative tools for accurate results.
Skilled professionals with in-depth industry knowledge.
Successful management of complex compliance challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
Pharmaceutical compliance involves adhering to laws, regulations, and guidelines that govern the pharmaceutical industry. It ensures that companies align their operations with industry standards, thereby safeguarding product safety and efficacy while maintaining data integrity.
The purpose of an audit is to systematically evaluate a company’s adherence to Regulatory standards and internal policies. Audits help identify areas for improvement, mitigate risks, and ensure that processes are effective in producing safe and compliant pharmaceutical products.
Validation in pharmaceuticals is the process of confirming that systems, processes, and equipment consistently meet predefined requirements. It is essential for ensuring compliance with Regulatory standards and for maintaining the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products throughout their lifecycle.
These processes are critical for ensuring product safety and efficacy, maintaining Regulatory adherence, enhancing quality assurance, supporting market access, and facilitating continuous improvement. They help companies meet stringent standards and build trust with stakeholders.
Challenges include navigating evolving regulations, ensuring data integrity, managing resource constraints, and maintaining proper documentation. Additionally, integrating innovative technologies and ensuring staff competency can complicate compliance efforts.
GxP audits are assessments conducted to ensure adherence to Good Practices (GxP) standards, which include Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), Good Clinical Practice (GCP), and Good Laboratory Practice (GLP). These audits help identify compliance gaps and enhance quality systems.
A GxP independent compliance audit is an objective evaluation of a company’s adherence to quality and Regulatory standards. Conducted by qualified auditors, it identifies risks and areas for improvement, enhancing compliance and product safety.
GxP audits provide impartial assessments, enhance Regulatory compliance, and identify areas for operational improvement. They help maintain high-quality standards and build trust with regulators and customers.
CSV ensures that computerized systems used in pharmaceuticals consistently produce reliable data and meet Regulatory requirements. It is vital for maintaining data integrity, mitigating risks, and ensuring patient safety throughout the product lifecycle.
CSV focuses on validating that a system meets Regulatory requirements and performs as intended, while CSA encompasses a broader approach that includes ongoing assurance of system performance and compliance throughout its lifecycle.













