
Combination products, which integrate drugs, devices, and/or biological products, have revolutionized healthcare by offering innovative therapeutic solutions. However, their unique nature presents significant Regulatory challenges. This comprehensive guide explores the intricate landscape of combination product regulation and provides strategies for successfully navigating these complex pathways.
Understanding Combination Products and Their Regulatory Framework
Combination products are medical products that combine two (2) or more regulated components - drugs, devices, or biologics - into a single entity. These innovative products can take various forms, such as drug-eluting stents, prefilled syringes, or transdermal patches. The Regulatory framework for combination products is primarily governed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, with similar approaches adopted by Regulatory bodies worldwide.
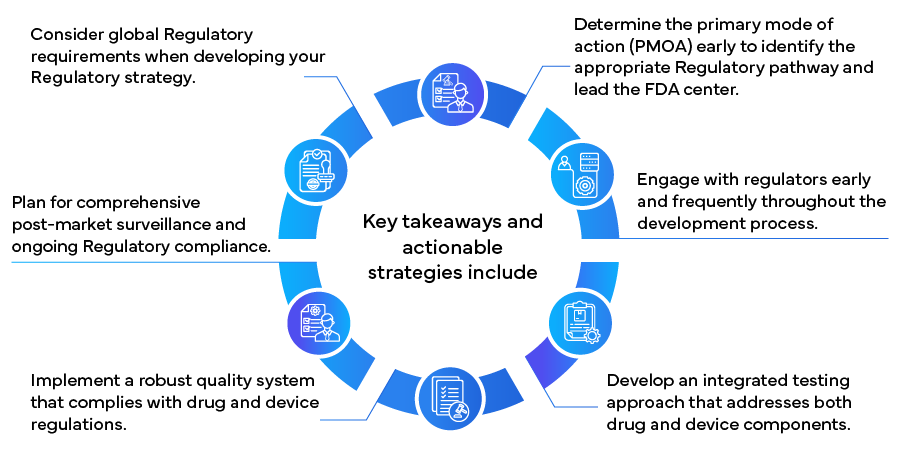
The FDA's Office of Combination Products (OCP) plays a crucial role in determining a combination product's primary mode of action (PMOA), which determines the Regulatory pathway and the lead FDA center responsible for review. The Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH), and Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) collaborate in the review process, emphasizing the need for an integrated approach to ensure combination product safety and efficacy.
Determining the Regulatory Pathway
One (1) of the most critical steps in developing a Regulatory strategy for combination products is determining the appropriate Regulatory pathway. This decision is primarily based on the product's PMOA. Here are key considerations:
- Primary Mode of Action (PMOA): Identify the single mode of action that provides the most important therapeutic action of the combination product.
- Lead Center Assignment: Based on the PMOA, the product will be assigned to CDER, CDRH, or CBER for primary review.
- Regulatory Submission Type: Depending on the lead center, the submission may take the form of a New Drug Application (NDA), Biologics License Application (BLA), or Premarket Approval (PMA).
- Request for Designation (RFD): If the PMOA is unclear, sponsors can submit an RFD to the OCP for a formal determination.
- Pre-Request for Designation (Pre-RFD): The OCP can receive a Pre-RFD for informal, non-binding feedback on classification and jurisdictional questions.
Understanding these factors is crucial for developing an effective Regulatory strategy tailored to your specific combination product.
Navigating Premarket Review Processes
The premarket review process for combination products can be complex, requiring careful planning and execution. Here are key strategies to navigate this process effectively:
- Early Engagement with Regulators: Initiate discussions with the FDA early in the development process through pre-submission meetings. These interactions can provide valuable guidance on Regulatory requirements, study designs, and potential challenges.
- Comprehensive Development Plan: Develop a robust plan that addresses the unique aspects of your combination product, including how the constituent parts interact and their combined effects on safety and efficacy.
- Integrated Testing Approach: Design preclinical and clinical studies that evaluate the individual components and the complete combination product. This approach should assess potential interactions and cumulative effects.
- Quality System Considerations: Implement a quality system that complies with drug (21 CFR 210/211) and device (21 CFR 820) regulations as appropriate for your product.
- Human Factors Engineering: Incorporate human factors studies to evaluate user interactions with the combination product, ensuring safe and effective use.
- Risk Management: Develop a comprehensive risk management plan that addresses potential risks associated with each component and their combination.
By adopting these strategies, sponsors can streamline the premarket review process and increase the likelihood of Regulatory success.
Addressing Post-Market Challenges
Regulatory responsibilities for combination products extend beyond market approval. Effective post-market surveillance and compliance are crucial for long-term success. Consider the following strategies:
- Integrated Pharmacovigilance: Implement a robust pharmacovigilance system that captures adverse events related to the combination product's drug and device components.
- Post-Market Studies: Plan and conduct post-market studies to gather additional safety and efficacy data, especially for novel combination products.
- Quality System Maintenance: Continuously update and maintain your quality system to ensure compliance with relevant regulations for drug and device components.
- Change Management: Establish a straightforward process for managing post-approval changes, considering the potential impact on the product's drug and device aspects.
- Regulatory Intelligence: Stay informed about evolving regulations and guidance documents related to combination products to ensure continued compliance.
By proactively addressing these post-market challenges, manufacturers can maintain Regulatory compliance and product safety throughout the product lifecycle.
Global Regulatory Considerations
As the market for combination products expands globally, understanding international Regulatory requirements becomes increasingly important. Consider these strategies for global Regulatory success:
- Regulatory Harmonization: Leverage international harmonization efforts, such as those by the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF), to streamline global Regulatory submissions.
- Market-Specific Requirements: Research and understand specific requirements for combination products in target markets, as regulations vary significantly between countries.
- Simultaneous Submissions: Consider simultaneous submissions to multiple Regulatory agencies to expedite global market access, where appropriate.
- Global Clinical Trials: Design clinical trials that meet the requirements of multiple Regulatory agencies to support global marketing applications.
- International Partnerships: Collaborate with local Regulatory experts or partners in target markets to navigate country-specific regulations and cultural considerations.
By adopting a global perspective in Regulatory strategy development, manufacturers can expand their market reach for combination products more effectively.
Conclusion
Navigating the Regulatory pathways for combination products requires a comprehensive understanding of complex Regulatory frameworks and strategic planning.
By implementing these strategies, manufacturers can more effectively navigate the complex Regulatory landscape for combination products, potentially accelerating time to market and ensuring long-term compliance and success. As the field of combination products continues to evolve, staying informed about Regulatory changes and maintaining flexibility in Regulatory approaches will be crucial for ongoing success in this innovative and rapidly growing healthcare sector.









