
What is the Role of Cybersecurity in Medical Devices?
The 510(k) clearance process is a Regulatory pathway used by the United States Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) to evaluate and provide clearance for the commercial distribution of medical devices. The process aims at ensuring that medical devices are safe and effective for patients’ use. The US FDA defines cybersecurity as “[t]he process of preventing unauthorized access, modification, misuse or denial of use, or the unauthorized use of information that is stored, accessed, or transferred from a medical device to an external recipient.”
Medical devices are increasingly getting connected to networks, and thus, are vulnerable to cybersecurity threats such as hacking, data breaches, and malware attacks. Addressing cybersecurity at the design and development stage is critical to ensure that medical devices have appropriate security controls in place. Threats and vulnerabilities cannot be eliminated, and reducing cybersecurity risks is especially challenging. If cybersecurity is not maintained properly, it could lead to compromised functionality of devices, loss of personal or medical data, and the possibility of security threats spreading to other interconnected networks or devices.
Incidents Caused by Compromised Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity incidents have caused medical devices and hospital networks to become inoperative, resulting in the disruption of patient care delivery across healthcare facilities in the US. Such cyberattacks and exploits may also lead to patients’ harm due to clinical hazards, for instance, a delay in diagnosis and/or treatment of patients.
Listed below are the key incidents across the healthcare sector that stress the importance of cybersecurity for patient safety.
- In 2017, The WannaCry ransomware attack affected hospital systems and medical devices across the globe.
- In 2020, a ransomware attack on a German hospital highlighted the potential eighty-three (83) impacts of delayed patient care as the attack forced patients to be diverted to another hospital.
The Key Cybersecurity Considerations for the 510(k) Clearance
The following are the general principles of cybersecurity for medical device manufacturers, according to the US FDA cybersecurity guidance specific to pre-market submissions.
- Quality System Regulation (QSR).: Manufacturers should address cybersecurity issues at the design and development stage of the medical device, as this can result in a more robust and efficient mitigation of patient risks. Manufacturers should establish cybersecurity-related design inputs for their device and a cybersecurity vulnerability and management approach as part of the software validation and risk analysis that is required by 21 CFR 820.30(g).
- Design Security: Device manufacturers must ensure that their products are designed with device security in mind. The US FDA will assess the adequacy of the security, based on the ability of the device to provide and implement security objectives such as authenticity, authorization, availability, confidentiality and security, and timely updatability throughout the system architecture.
- Transparency: A lack of cybersecurity information on the device, such as information necessary to integrate the device into the use environment, as well as information needed by users to maintain cybersecurity over the lifecycle of the device, has the potential to affect its safety and efficacy. To address these concerns, it is important for device users to have access to the information pertaining to cybersecurity controls, potential risks, and other relevant information.
- Submission Documentation: Device cybersecurity design and documentation is expected to scale with the cybersecurity risk of a device. Manufacturers should consider the larger system in which a device may be used.
Figure 1: Common Cybersecurity Challenges and Solutions 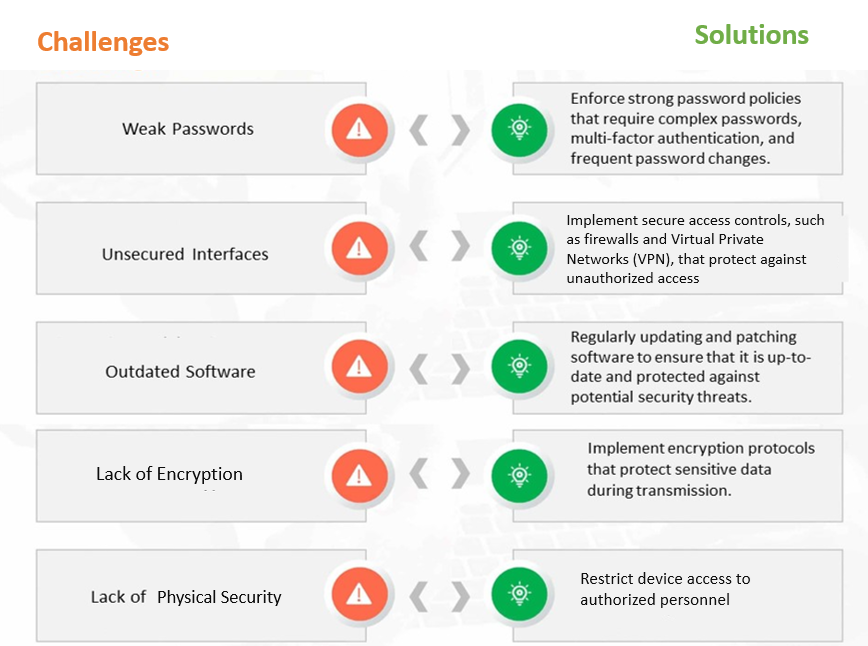
Conclusion
To summarize, cybersecurity in medical devices is crucial to ensure patient safety and prevent incidents that may disrupt healthcare delivery. The US FDA cybersecurity regulations emphasize the need for manufacturers to address cybersecurity issues during the design and development of medical devices and provide transparent information on cybersecurity controls. The QSR, design security, transparency, and submission documentation are key considerations for the 510(k) clearance. It is also important to address common cybersecurity challenges such as vulnerabilities in third-party components and ransomware attacks and implement solutions such as robust risk analysis and regular software updates.
To experience a hassle-free and compliant 510(k) clearance process, get in touch with our Regulatory experts. Stay informed! Stay compliant!









