Comprehensive Sustainability Regulatory Services for Global Compliance
Browse Topics
- Introduction to Sustainability
- Key EU Sustainability Regulations
- Circular Economy and Sustainability
- Sustainability lifecycle management Across the Product Lifecycle
- Sustainability in the Healthcare Industry
- Corporate Sustainability solutions
- Impact of Sustainability on Market Access
- Future of Sustainability
- Freyr’s Comprehensive Sustainability Solutions
- Why Choose Freyr for Sustainability Regulatory Services
Introduction to Sustainability
Last updated on: December, 2024
Sustainability regulations are increasingly becoming a cornerstone of modern business practices, driven by the urgent need to address environmental challenges and promote social responsibility.
Understanding Global Sustainability Regulations: Definitions & Principles
Sustainability regulations encompass a wide array of laws, guidelines, and standards designed to promote environmentally friendly practices and ensure social responsibility within businesses. These regulations aim to minimize environmental impact, enhance resource efficiency, and protect human rights.
Key principles include:

Circular Economy
This model contrasts sharply with the traditional linear economy of "take-make-dispose." Instead, it emphasizes keeping products and materials in use for as long as possible, thereby reducing waste and conserving resources
Environmental Protection
Regulations often focus on reducing pollution, conserving biodiversity, and mitigating climate change impacts. They encourage businesses to adopt sustainable practices throughout their operations
Social Responsibility
Many sustainability regulations also address labor conditions and community welfare, ensuring that businesses operate ethically and contribute positively to society.
Importance of Sustainable Practices in Business
The integration of sustainable practices into business operations is not merely a regulatory requirement; it offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Reputation: Companies that prioritize sustainability often enjoy a better public image, which can lead to increased customer loyalty and brand trust.
- Market Competitiveness: As consumers become more environmentally conscious, businesses that adopt sustainable practices can differentiate themselves in the marketplace. Research shows that consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for eco-friendly products.
- Operational Efficiency: Sustainable practices often lead to cost savings through improved resource efficiency. For instance, reducing energy consumption not only lowers costs but also helps in carbon footprint reduction.
- Risk Management: Compliance with sustainability regulations helps companies avoid legal penalties and reputational damage associated with environmental violations.
Need for Sustainability Regulations
Sustainability regulations serve as essential tools for fostering responsible business practices the necessity for sustainability regulations stems from several critical factors:
- Environmental Degradation: The ongoing depletion of natural resources and rising pollution levels necessitate regulatory frameworks that enforce responsible usage and conservation efforts.
- Consumer Demand: There is a growing consumer preference for sustainable products. Surveys indicate that a significant portion of consumers actively seek out brands committed to eco-friendly practices.
- Global Agreements: International agreements such as the Paris Agreement highlight the global commitment to combat climate change. Countries are increasingly implementing regulations that align with these global goals, compelling businesses to adapt accordingly.
- Corporate Accountability: As stakeholders demand greater transparency regarding environmental impact, companies must adhere to sustainability regulations to demonstrate their commitment to responsible governance.
Key EU Sustainability Regulations
- 30 December 2025Regulation on Deforestation Risk Commodities
- Implementation: 30 December 2025
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: Agricultural commodities (e.g., soy, palm oil, coffee), timber, paper, pulp products, packaging
Obligations: Direct impact on raw materials
- February 2025Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation
- Implementation: February 2025
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: All packaging materials (e.g., plastic, paper, metal, glass), consumer and industrial packaging
- Obligations: Direct impact on packaging materials and disposal/recycling
- 30 March 2024Green Sustainability Claims and Labelling
- Implementation: 30 March 2024
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: All consumer goods (including biocides)
- Obligations: Direct impact on labels and sustainability claims
- 16 March 2024Net-Zero Industry Act
- Implementation: 16 March 2024
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: Renewable energy technologies, energy storage systems, carbon capture and storage, energy-efficient industrial equipment
- Obligations: Direct impact on manufacturing and claims
- 28 February 2024Directive on Empowering Consumers for the Green Transition
- Implementation: 28 February 2024
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: Eco-labeled products, consumer electronics, household appliances, textiles, clothing, food products
- Obligations: Direct impact on raw materials, packaging, labels, and disposal
- 22 March 2023Common Rules to Promote the Repair of Goods for Consumers
- Implementation: 22 March 2023
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: Consumer electronics, household appliances, textiles, footwear, furniture
- Obligations: Encouraging the repairability of goods
- 1 January 2023The Anti-Waste Law in France
- Implementation: 1 January 2023
- Region: France (EU)
- Products Impacted: Plastics, packaging, single-use accessories, textiles, electronics, construction materials
- Obligations: Direct impact on raw materials, formulation, packaging, labels, claims, manufacturing, and disposal (sustainability regulati…)
- 19 December 2022Improving Classification, Labelling and Packaging of Hazardous Chemicals
- Implementation: 19 December 2022
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: Industrial chemicals, consumer chemicals (e.g., cleaning products), pesticides, and biocides
- Obligations: Direct impact on raw materials and formulation
- 30 November 2022Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for Packaging
- Implementation: 30 November 2022
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: Consumer goods packaging (e.g., food, beverages, BPC), industrial and commercial packaging, single-use plastic items
- Obligations: Direct impact on packaging materials and disposal
- 29 July 2021European Climate Law
- Implementation: 29 July 2021
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: Energy-intensive industries (steel, cement), automotive, building materials, consumer products with high carbon footprints
- Obligations: Direct impact on manufacturing processes and claims
- 19 April 2021Organic Action Plan
- Implementation: 19 April 2021
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: Organic food and beverages, organic farming inputs (e.g., seeds, fertilizers), organic textiles
- Obligations: Direct impact on raw materials and formulation
- 19 April 2021European Industrial Strategy
- Implementation: 19 April 2021
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: High-tech industries (aerospace, automotive), manufacturing sectors, renewable energy technologies, digital and green sustainability technologies
- Obligations: Direct impact on manufacturing and claims
- 27 March 2021Food Contact Materials
- Implementation: 27 March 2021
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: Food packaging, kitchenware, food storage containers, utensils, and appliances that come into contact with food
- Obligations: Direct impact on packaging materials
- 14 October 2020Chemicals Strategy for Sustainability
- Implementation: 14 October 2020
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: Industrial chemicals, consumer products (e.g., detergents, BPC), pharmaceuticals, pesticides, plastics
- Obligations: Direct impact on raw materials and formulation
- May 2020Farm to Fork Strategy
- Implementation: May 2020
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: Food and beverages, agricultural products, animal feed, pesticides, fertilizers
- Obligations: Direct impact on raw materials, labels, and disposal
- 12 June 2019Single-Use Plastic Bans
- Implementation: 12 June 2019
- Region: EU
- Products Impacted: Single-use plastic items (e.g., straws, cutlery, plates), food packaging, beverage containers, plastic bags
- Obligations: Direct impact on packaging and disposal
Circular Economy and Sustainability
Principles of the Circular Economy
A circular economy is based on principles of resource efficiency, minimizing waste, and maintaining the value of products and materials for as long as possible. Key principles include:
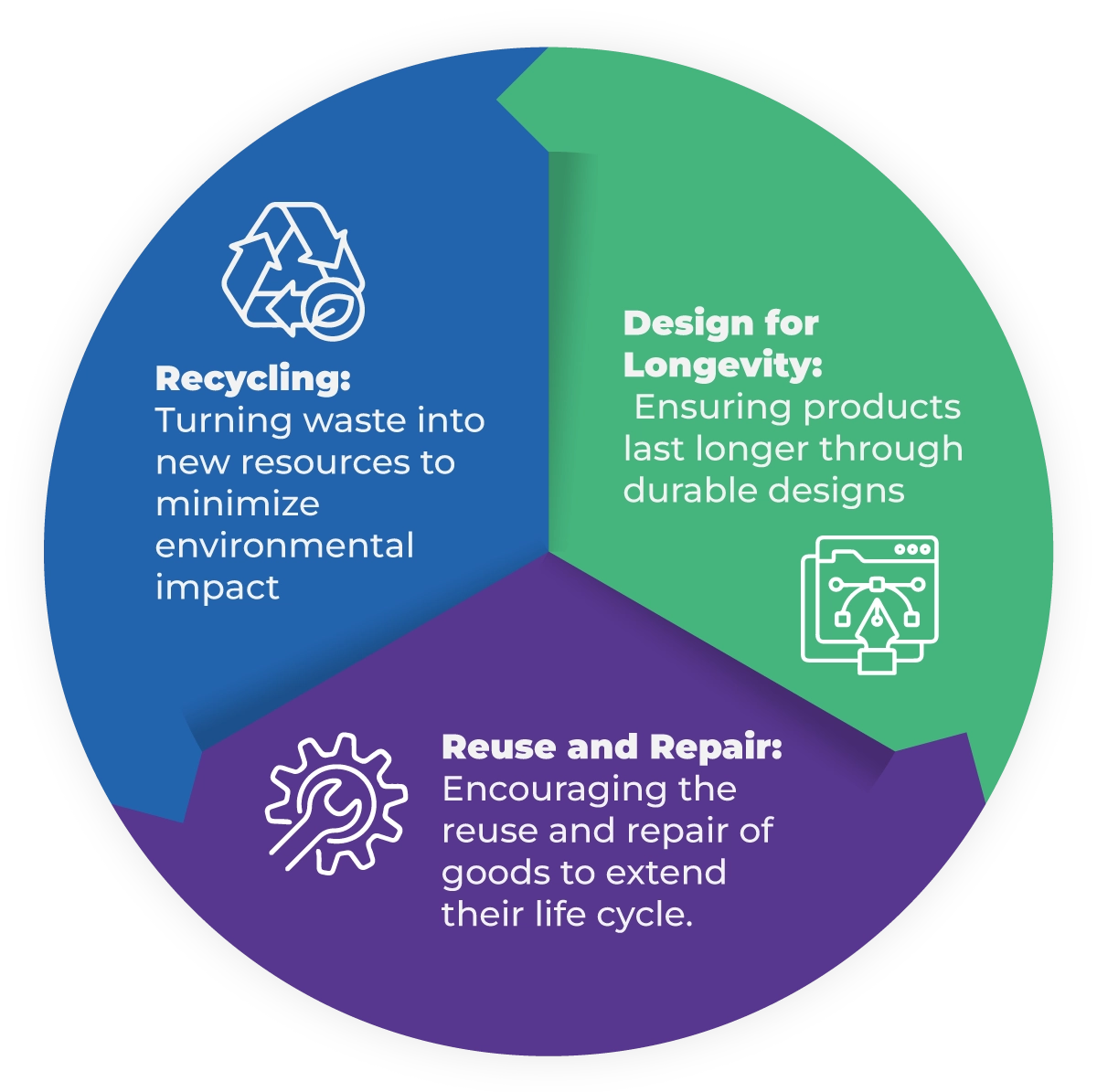
Transitioning from Linear to Circular Economies
Traditional business models operate on a 'take-make-dispose' approach, which leads to resource depletion and environmental degradation. The circular economy flips this model by focusing on reducing waste and keeping materials in circulation for longer, benefiting both the environment and businesses through resource optimization .
How Circularity Impacts Business Models
Incorporating circular economy principles impacts business models by:
- Reducing Waste: Implementing recycling and reuse systems decreases production waste and operational costs.
- Innovative Product Design: Companies are encouraged to design products that are easier to disassemble, repair, and recycle.
- New Revenue Streams: Circular models open up opportunities for new business ventures in the secondary market for refurbished or remanufactured goods.
Sustainability lifecycle management Across the Product Lifecycle
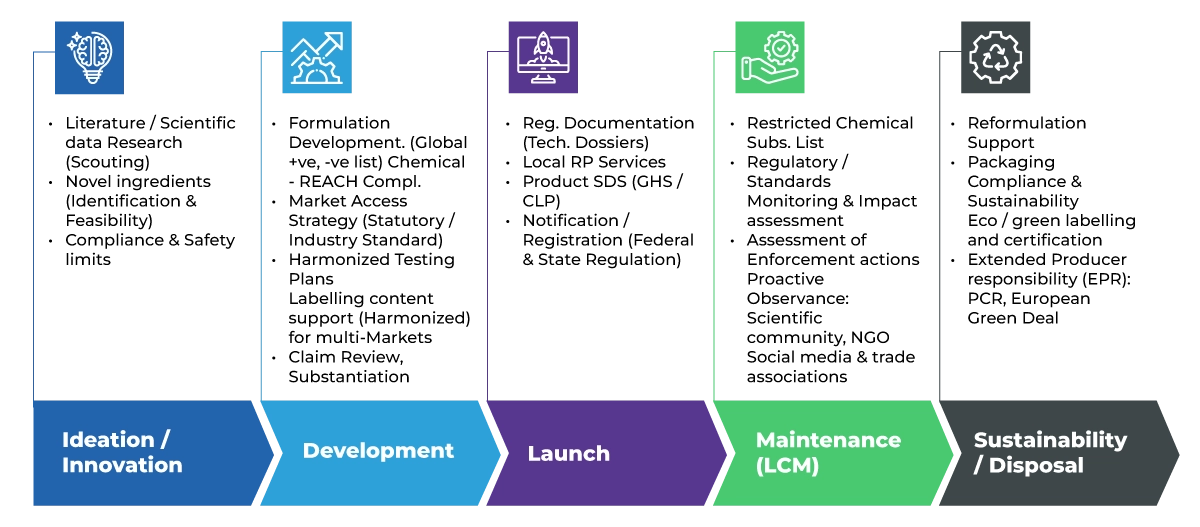
The Environmental Impact of the Pharmaceutical Industry: A Call for Sustainable Practices
The healthcare sector significantly impacts the environment through waste disposal, CO2 emissions, plastic usage, and various forms of pollution, including air and water contamination. Additionally, energy consumption related to transportation and the refrigeration of medications further exacerbates the industry's carbon footprint. Alarmingly, the carbon footprint of the pharmaceutical industry is 55% higher than that of the automotive industry.
Sustainable Product Design & Development
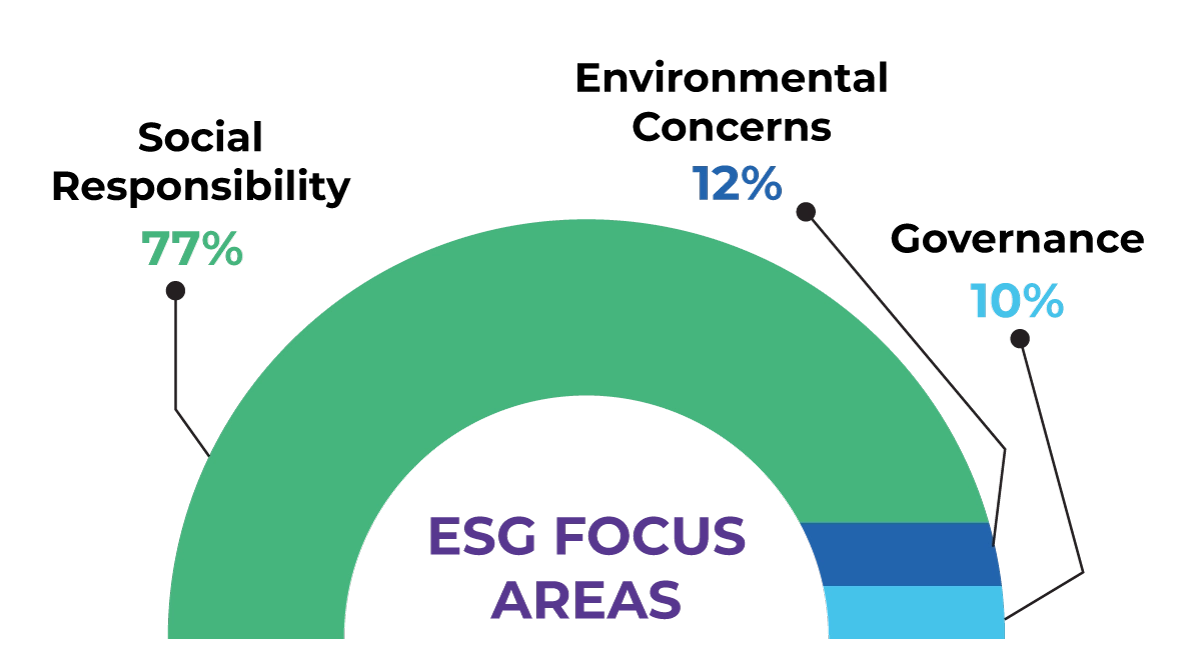
The shift towards sustainable product design begins with innovative practices that reduce environmental impact from the outset. By incorporating eco-friendly materials and sustainable methods, pharmaceutical companies can enhance their overall Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) profile. Recent studies indicate that over 77% of pharmaceutical ESG initiatives focus on social aspects, leaving only 12% directed at environmental concerns. Prioritizing sustainable design not only meets regulatory demands but also positions companies favorably in the marketplace.
Packaging Compliance and Innovation for Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics, and Consumer Products
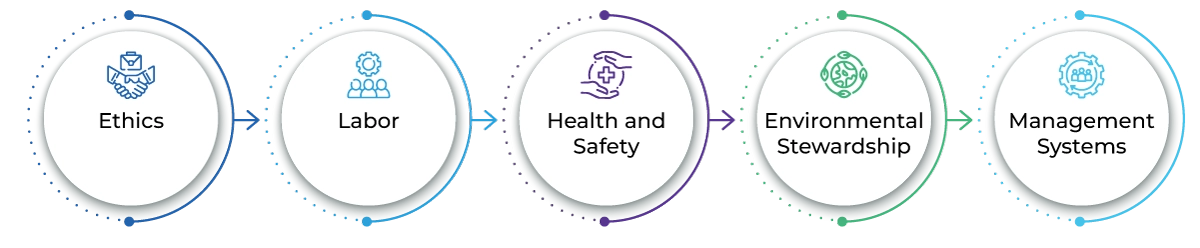
As regulatory bodies worldwide implement stricter regulations on sustainable packaging, the demand for compliant and innovative solutions is surging. The Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Initiative established five key principles in 2006, guiding industry expectations regarding ethics, labor, health and safety, environmental stewardship, and management systems.
Key-Principles-for-Sustainable-Packaging
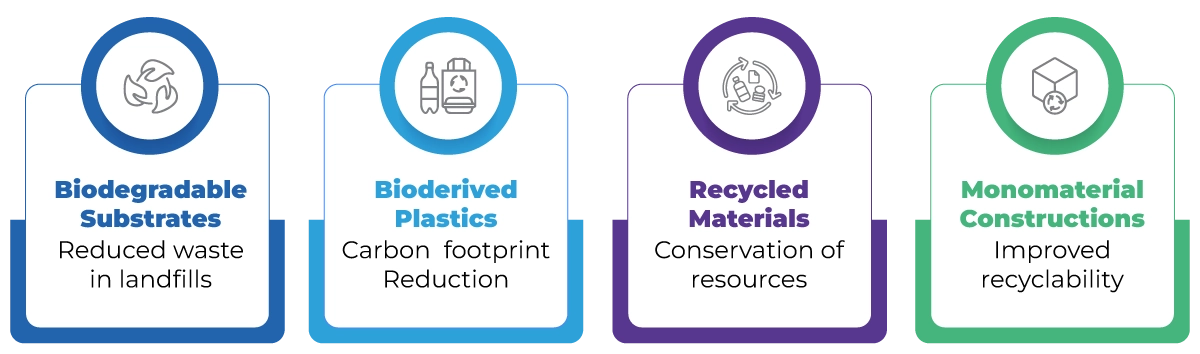
Current initiatives in Europe aim to reduce microplastics and transition from hardcopy information leaflets to digital formats, significantly minimizing packaging waste. With a rising consumer focus on sustainability, pharmaceutical and cosmetic companies must prioritize innovative packaging solutions. This includes adopting biodegradable substrates, bioderived plastics, recycled materials, and monomaterial constructions. For instance, since April 2022, the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) mandates that procurements include a minimum of 10% net zero and social value weighting, compelling suppliers to enhance their sustainability efforts.
End-of-Life Solutions: Recycling and Reuse
Effective end-of-life solutions are crucial for reducing the environmental impact of pharmaceutical products. Implementing recycling and reuse strategies can help mitigate waste and promote a circular economy. As regulations evolve, companies are increasingly encouraged to create packaging that is recyclable or reusable, thus reducing landfill contributions and promoting sustainability.
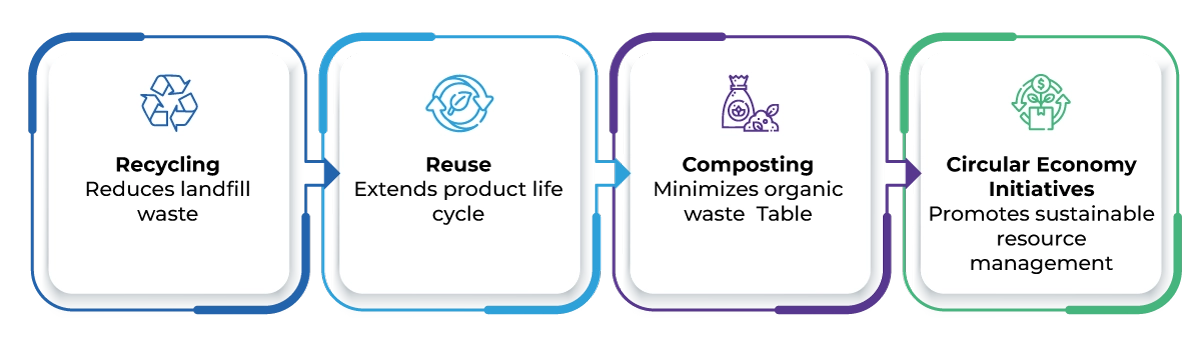
As the industry responds to the growing pressure from consumers and regulators, the demand for innovative and sustainable packaging solutions will continue to rise. By prioritizing sustainable product design, compliant packaging innovation, and effective end-of-life strategies, the pharmaceutical and consumer product sectors can lead the charge toward a more sustainable future.
Sustainability in the Healthcare Industry
Environmental Impact of Healthcare Practices
The pharmaceutical industry is increasingly called upon to adopt environmentally friendly packaging solutions as consumer awareness of sustainability rises. In the UK, the National Health Service (NHS) mandates that procurements incorporate a minimum of 10% net zero and social value weighting, emphasizing the urgency for transformation. This regulatory shift fuels demand for biodegradable substrates, bioderived plastics, recycled materials, and monomaterial constructions, aligning industry practices with evolving regulatory requirements and consumer expectations.
| Regulatory Mandates | Requirements |
|---|---|
| NHS Procurement Guidelines | Minimum 10% net zero and social value weighting |
| EU Regulations | Reduction of microplastics |
| Global Standards | Adoption of biodegradable materials |
Green Solutions in Pharmaceutical Packaging
The momentum toward sustainable packaging in pharmaceuticals is accelerating due to regulatory mandates and growing consumer demand. Innovations like biodegradable substrates, bioderived plastics, and recycled materials are essential for mitigating environmental impact. Additionally, the adoption of monomaterial constructions enhances recyclability.
As the industry addresses these challenges, developing innovative packaging solutions will be critical in promoting sustainability and reinforcing corporate responsibility.
Corporate Sustainability solutions
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) vs. Sustainability
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has evolved from a profit-centric approach to one that prioritizes community and environmental impact. This shift emphasizes strategic partnerships that align with business interests and social goals. Regulatory frameworks like the EU Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) and the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) mandate transparency, pushing companies to integrate sustainability into their core operations and decision-making processes, thus enhancing their social license to operate.
Benefits of Corporate Sustainability for Long-term Success
Corporate sustainability provides critical advantages, including enhanced reputation, increased customer loyalty, and improved employee engagement. By conducting materiality assessments to identify key ESG issues and setting specific sustainability goals with measurable Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), companies can drive innovation and efficiency.
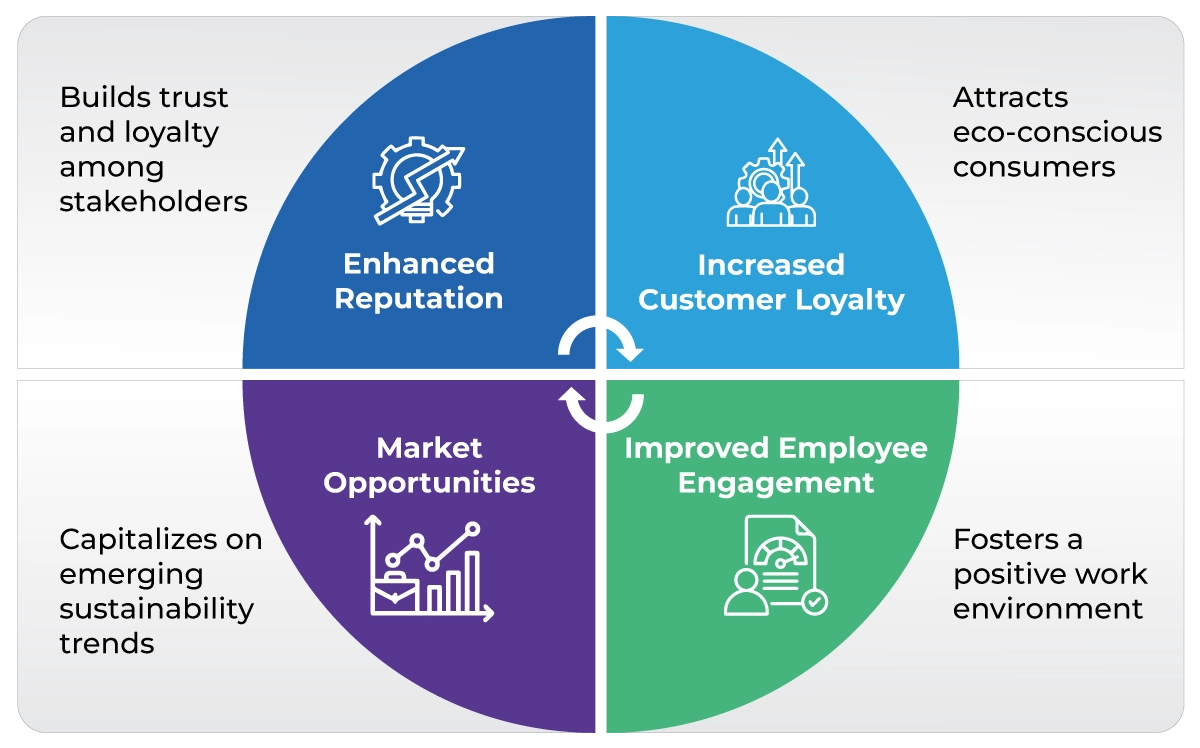
This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also positions organizations to capitalize on emerging market opportunities, ultimately leading to sustainable financial performance.
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) Reporting
Effective ESG reporting is vital for demonstrating accountability and building stakeholder trust. Companies should adhere to established standards like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) to ensure comprehensive data collection on environmental, social, and governance factors. Engaging stakeholders and obtaining third-party assurance enhances report credibility, while transparent communication through accessible channels fosters stronger relationships with investors, customers, and the community, ultimately supporting long-term success.
| ESG Reporting Standards | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) | Framework for sustainability reporting |
| Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) | Sector-specific standards for ESG disclosure |
Impact of Sustainability on Market Access
Sustainability as a Competitive Advantage
Sustainability provides a competitive edge by reducing costs, improving efficiency, and attracting eco-conscious consumers. Companies that adopt circular economy principles, such as resource efficiency and product reuse, reduce waste while enhancing operational performance. This approach strengthens brand reputation and appeals to investors and customers, aligning with regulatory demands.
Global Market Entry: Sustainable Products
Entering global markets with sustainable products requires environmental compliance with environmental regulations like the EU Green Deal. Companies must ensure that their products and packaging meet high environmental standards, such as using recyclable materials and reducing emissions. This facilitates market access and strengthens brand positioning as sustainability leaders.
Case Examples of Companies Succeeding with Sustainability
PharmaGreen Co. uses recycled plastics in its packaging, reducing environmental impact while maintaining safety standards. AquaMed Solutions’ refillable liquid medication system saves over 500,000 plastic bottles from landfills annually. These companies showcase how sustainability enhances environmental compliance and builds customer loyalty.
Future of Sustainability
Innovations Driving Sustainability in Business
Circular economy models, eco-design, and sustainable materials are transforming businesses. Companies are using recycled, biodegradable packaging and adopting digital solutions to reduce waste and meet regulatory demands, driving sustainable business practices.
How Businesses Can Prepare for Future Regulations
Businesses should monitor regulatory trends like the EU Green Deal and adjust product development, packaging, and supply chains. Implementing due diligence systems and resource efficiency strategies helps companies stay ahead of regulations and avoid penalties.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Practices
Technology enables sustainable practices through smart sensors, data analytics, and digital tools for tracking resource use and environmental compliance. Innovations like digital product passports and AI help streamline operations, reduce waste, and improve supply chain transparency.
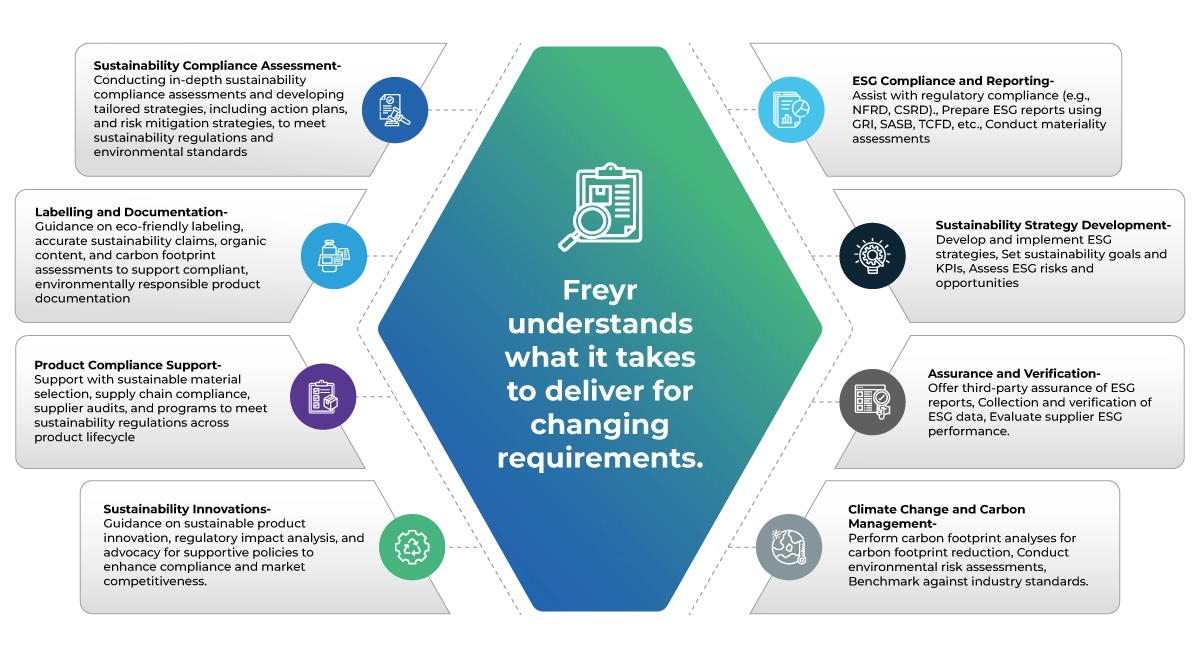
Freyr’s Comprehensive Sustainability Solutions
Compliance & Regulatory Support
Freyr helps businesses navigate sustainability regulations like the EU Green Deal, ensuring compliance and reducing risks.
Packaging & Ecolabeling
Freyr offers expertise in sustainable packaging and labeling, guiding companies on biodegradable packaging materials and meeting global standards.
Support Across the Product Lifecycle
Freyr provides end-to-end assistance for sustainability lifecycle management, from development to compliance, integrating sustainability at every stage and ensuring regulatory alignment.
Why Choose Freyr for Sustainability Regulatory Services