Global Pharma Regulatory Labeling Services
Leverage a decade of expertise with our Regulatory Labeling services, covering new product authorizations, Health Authority submissions, post-approvals, CMC, and lifecycle management. Our focus on global and local excellence ensures strategic creation and updates for essential labeling documents like IBs, CDS, and CCDS, guaranteeing compliance and success in the pharmaceutical industry.
Browse Topics
- What is Regulatory Labeling?
- Why is Regulatory Labeling Important in Pharma?
- What is the Labeling Approval Process?
- What Are Common Challenges in Regulatory Labeling?
- What are the key regulations governing Pharma labeling?
- How can a Regulatory partner help in achieving compliance with the labeling requirements?
- How Can Companies Get Started with Regulatory Labeling Services?
- Can Regulatory Labeling Services Assist in Post-market Monitoring?
- Why choose Freyr?
- Our Services
What is Regulatory Labeling?
Last updated on: August, 2024
Pharmaceutical Regulatory labeling involves the creation, review, and management of critical documents that communicate essential product information to stakeholders, ensuring compliance with global Regulatory standards. Core components include the Core Data Sheet (CDS) and Company Core Data Sheet (CCDS), derived from sources such as Investigational Brochures and post-marketing data. This process is pivotal in conveying safety and efficacy information on country-specific labels and aligning with Health Authority (HA) requirements.
With a focus on global harmonization, pharmaceutical Regulatory labeling addresses evolving Regulatory demands, encompassing new product authorizations, HA submissions, post-approvals, and lifecycle management. Precision and adherence to evolving guidelines are crucial for successful pharmaceutical Regulatory labeling, influencing a product's market authorization, safety profile, and overall Regulatory viability.

Freyr, a leader in end-to-end drug Regulatory labeling services, boasts a dedicated team of over 180 global labeling experts, excelling in drafting crucial documents such as Investigational Brochures (IB), Developmental Core Data Sheets, and Developmental Core Safety Information. Leveraging artificial intelligence enhances accuracy and expedites data sheet implementation and review. With a streamlined CCDS template and precision-driven processes, Freyr's comprehensive services effectively meet the dynamic needs of the pharmaceutical industry, providing unparalleled support for labeling compliance and Regulatory success.
Why is Regulatory Labeling Important in Pharma?
- Ensuring Patient Safety and Information Communication: Regulatory labeling is crucial for patient safety. Labels provide essential information about drug usage, dosages, side effects, and contraindications. Patients, prescribing physicians, healthcare professionals, and caregivers rely on these labels to make informed decisions. Clear and accurate labeling reduces the risk of medication errors, adverse events, and misuse.
It ensures that patients receive the right treatment and understand its proper use. Moreover, Regulatory authorities demand that each pharmaceutical product on the market must have labeling to communicate treatment information effectively. - Compliance and Risk Mitigation: Compliance with labeling regulations is not just a formality; it’s a legal requirement. Regulatory bodies such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and others mandate accurate and comprehensive labeling. Non-compliance can result in Regulatory fines, damage to brand reputation, and even temporary production line shutdowns. Pharmaceutical companies must demonstrate that their labeling processes, methods, tests, and equipment are capable of consistently producing safe and effective products. Properly validated labeling mitigates risks and ensures adherence to good manufacturing practices (GMP).
- Market Access and Global Harmonization: Well-structured labels facilitate global market access. Consistent labeling across regions streamlines processes, reduces redundancies, and aligns with harmonized standards. As international regulators adopt GMP validation requirements, including serialization, pharmaceutical supply chains face increasing complexity. Companies that prioritize labeling compliance establish trust, enhance market acceptance, and position themselves for success in a competitive landscape.
What is the Labeling Approval Process?
The labeling approval process in the pharmaceutical industry involves multiple stages to ensure that all drug-related information is accurate, compliant, and clear for both healthcare providers and patients. It starts with drafting the label content, which includes details on dosage, administration, safety, and warnings. Regulatory and medical teams then internally review this draft to ensure it aligns with local and international Regulatory standards. Once finalized, the label is submitted to health authorities for approval, where it undergoes rigorous scrutiny to verify its compliance with safety and efficacy requirements. Only after receiving official approval can the label be used in marketing the drug.
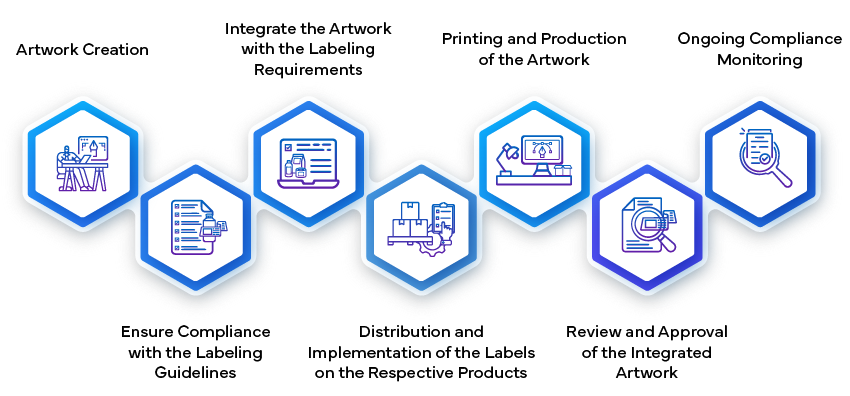
- Creating and Submitting the Label:
- Initial Data Gathering: Pharmaceutical companies compile all relevant data for the drug label. This includes information on efficacy, safety, dosages, indications, contraindications, and potential risks. The label serves as a critical communication tool for healthcare professionals and patients.
- Submission to Regulatory Authorities: The company submits the label data to Regulatory bodies, such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or European Medicines Agency (EMA). These agencies evaluate the data to ensure that the drug provides benefits that outweigh its known and potential risks for the intended population.
- Contextual Analysis: Reviewers analyze the target condition or illness for which the drug is intended. They consider the existing treatment landscape, weighing the drug’s risks against its benefits. For instance, a drug treating a life-threatening disease with no alternative therapy may be approved even if the risks would be unacceptable for a non-life-threatening condition.
- Clinical Data Assessment: FDA reviewers evaluate clinical benefit and risk information submitted by the drug maker. They account for any uncertainties arising from imperfect or incomplete data. Typically, the agency expects results from well-designed clinical trials to validate the drug’s efficacy and safety.
- Establishing the Artwork:
- Once the label content is approved, the next step is creating the label artwork. This involves designing the visual elements, layout, fonts, and graphics. The artwork must align with Regulatory guidelines and accurately represent the information on the label.
- The label artwork undergoes internal reviews within the pharmaceutical company to ensure consistency and compliance. It includes details like dosage instructions, warnings, storage conditions, and contact information.
- The final artwork is submitted to Regulatory authorities for approval. This step ensures that the visual presentation of the label adheres to quality standards and effectively communicates critical information to users.
- Manufacturing and Implementation:
- Once approved, the label artwork becomes an integral part of the drug packaging. Manufacturers ensure that labels are correctly attached to each product unit (e.g., bottles, blister packs, vials).
- Quality control procedures verify that labels meet specifications, including accurate content, legibility, and adherence to design guidelines.
- The label serves as a bridge between the pharmaceutical company, Regulatory agencies, healthcare providers, and patients. It plays a vital role in ensuring safe and effective medication use throughout the product’s lifecycle.
What Are Common Challenges in Regulatory Labeling?
Common challenges in Regulatory labeling include keeping up with evolving Regulatory requirements, managing multilingual labeling, and ensuring consistency across diverse product portfolios. The dynamic nature of Regulatory standards for pharmaceutical labeling demands continuous vigilance to stay updated with the latest requirements. Adapting to changing regulations and promptly implementing necessary updates to labeling content and format is essential to maintain compliance and ensure patient safety.
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Evolving Regulatory Requirements | Coping with continuously changing regulations and guidelines, necessitating constant updates to labeling documentation. |
| Global Harmonization | Ensuring consistency in product information across diverse regions, aligning with the varied requirements of different health authorities. |
| Post-marketing Data Integration | Managing the incorporation of post-marketing safety and efficacy data into labeling, maintaining accuracy and relevance. |
| Compliance with Local Labeling Standards | Adhering to specific labeling standards of individual countries, addressing linguistic, cultural, and formatting variations. |
| Efficient Labeling Change Management | Streamlining processes for tracking, implementing, and documenting labeling changes promptly and accurately. |
Multilingual labeling poses a significant challenge for pharmaceutical companies operating in global markets. Accurately translating labeling content into multiple languages while adhering to regional linguistic and Regulatory nuances requires attention to detail and robust translation management processes. Ensuring consistency and clarity across different language versions is crucial for effectively communicating vital information to diverse patient populations.
Maintaining consistency across product portfolios presents another common challenge in Regulatory labeling. Pharmaceutical companies often manage several products with varying labeling requirements, formulations, and indications. Achieving coherence and compliance across diverse product lines while meeting specific Regulatory demands for each product necessitates efficient processes and systems to ensure uniformity in labeling content, format, and messaging.
What are the key regulations governing Pharma labeling?
Pharmaceutical labeling is governed by a complex set of regulations designed to ensure the safety, efficacy, and accurate use of medications. A few of them are listed below:
US FDA (United States Food and Drug Administration)
The US FDA governs pharmaceutical labeling through a stringent set of regulations outlined in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21. These regulations require that labels provide comprehensive information, including drug indications, usage instructions, contraindications, and potential side effects. The FDA emphasizes the importance of clear, precise, and unambiguous language to ensure patient safety and informed decision-making by healthcare providers. Additionally, the FDA's labeling requirements extend to various aspects such as packaging, inserts, and electronic labeling, ensuring that all information is accessible and standardized across different formats. Compliance with these regulations is mandatory for drug approval and continued market presence in the United States.
EMA (European Medicines Agency)
The EMA oversees pharmaceutical labeling in the European Union through directives and guidelines designed to harmonize labeling across member states. The European Commission Directive 2001/83/EC is central to these efforts, specifying the requirements for the Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC), patient information leaflets, and packaging labels. The EMA ensures that labeling includes essential information for both healthcare professionals and patients, promoting safe and effective medication use across the EU (European Union). Additionally, the labeling must be available in the official languages of the member states where the drug is marketed, reflecting the EMA's commitment to accessibility and patient-centered care.
TGA (Therapeutic Goods Administration)
In Australia, the TGA is responsible for regulating pharmaceutical labeling under the Therapeutic Goods Act 1989. The TGA's guidelines mandate that drug labels provide clear, accurate, and comprehensive information about the product, including its ingredients, indications, dosage, and potential risks. The labeling requirements are designed to protect public health by ensuring that consumers and healthcare professionals have the information necessary to use medications safely and effectively. The TGA also places significant emphasis on the readability of labels, requiring that they be written in plain English, and that critical information is prominently displayed to prevent misuse and medication errors.
Health Canada
Health Canada regulates pharmaceutical labeling through a framework that prioritizes the safety and well-being of patients and healthcare providers. The Food and Drugs Act and its associated regulations outline the requirements for drug labels, which must include detailed information on the product's composition, indications, contraindications, and potential side effects. Health Canada also mandates that labels be bilingual, presented in both English and French, to accommodate the country's linguistic diversity. Furthermore, Health Canada regularly updates its labeling requirements to reflect new scientific evidence and evolving public health needs, ensuring that the labeling remains relevant and effective in promoting safe medication use.
PMDA (Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency)
The PMDA, Japan's Regulatory authority, oversees pharmaceutical labeling in accordance with the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law and related guidelines. The PMDA requires that drug labels provide comprehensive information, including indications, dosage instructions, and potential adverse effects, in a format that is easily understood by both healthcare professionals and patients. The PMDA also mandates that labels include warnings and precautions specific to the Japanese population, considering factors such as genetic differences and cultural practices. This approach ensures that medications are used safely and effectively in Japan, with labeling tailored to the unique needs of the local market.
NMPA (National Medical Products Administration)
In China, the NMPA governs pharmaceutical labeling through a Regulatory framework that emphasizes accuracy, clarity, and safety. The Drug Administration Law of the People's Republic of China outlines the requirements for drug labels, which must include information on the drug's indications, dosage, contraindications, and potential side effects. The NMPA also requires that labeling be presented in simplified Chinese to ensure accessibility to the local population. Additionally, the NMPA mandates that labels undergo rigorous review during the drug approval process to ensure compliance with national standards and to protect public health by preventing medication errors and misuse.
How can a Regulatory partner help in achieving compliance with the labeling requirements?
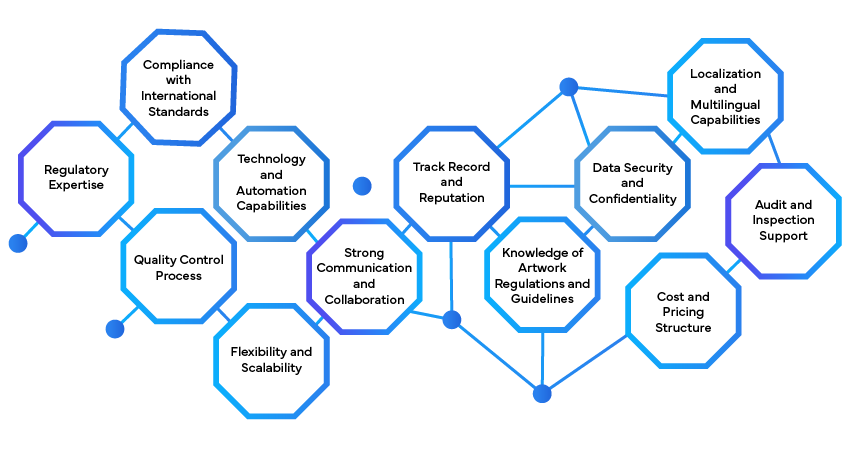
A Regulatory partner is instrumental in achieving compliance with labeling requirements by offering specialized expertise and comprehensive support. They guide companies through the complex Regulatory landscape, ensuring that labeling materials—including packaging, inserts, and electronic labels—adhere to the specific requirements of different health authorities such as the US FDA, EMA, TGA, Health Canada, PMDA, and NMPA. This involves understanding and applying the latest regulations, which can vary significantly across regions, to ensure that all product information is accurate, complete, and compliant.
Moreover, a Regulatory partner helps streamline the labeling process by providing critical services such as content creation, review, and validation. They assist in drafting and revising labeling content to align with Regulatory standards and ensure that all necessary information is included, from ingredient lists and usage instructions to safety warnings and storage conditions. This reduces the risk of errors and omissions that could lead to Regulatory delays or market withdrawals, speeding up the time-to-market for new products.

Additionally, a Regulatory partner supports companies in maintaining ongoing compliance by monitoring Regulatory updates and implementing changes as needed. They offer strategic advice on adapting labels to new guidelines or emerging market requirements, helping companies avoid non-compliance issues and ensuring that their products remain in line with current regulations. By leveraging their expertise and staying abreast of Regulatory changes, a Regulatory partner helps companies navigate the dynamic labeling landscape efficiently and effectively.
How Can Companies Get Started with Regulatory Labeling Services?
To get started with Regulatory labeling services, companies should first assess their specific labeling needs based on the target markets and Regulatory requirements. Next, they should partner with a reliable Regulatory service provider with expertise in global labeling standards. This provider can assist in drafting, reviewing, and updating labels to ensure compliance. Additionally, implementing a centralized labeling management system helps streamline the process, ensuring consistency across all product labels. Regular audits and updates are essential to keep labels aligned with evolving regulations.
Assess Regulatory Needs:
- Identify the specific Regulatory requirements applicable to your product and target markets.
- Understand critical documents, such as Core Data Sheets (CDS), Investigational Brochures (IB), and local labeling requirements.
Select a Regulatory Labeling Partner:
- Research and choose a reputable Regulatory labeling service provider with expertise in your industry.
- Consider factors such as experience, global Regulatory knowledge, and the ability to handle diverse labeling challenges.
Define Project Scope:
- Clearly outline the scope of your Regulatory labeling project, including the type of services required (e.g., IB drafting, CCDS creation, labeling compliance review).
- Establish timelines, milestones, and deliverables for each phase of the project.
Collaborate on Data Collection:
- Collaborate closely with your chosen Regulatory labeling partner to gather essential data, including clinical trial information, safety and efficacy data, and any post-marketing surveillance data.
Initiate Document Creation and Review:
- Begin the creation or revision of crucial documents such as IBs, DCDS, CCDS, and local labeling content.
- Facilitate regular reviews and feedback sessions to ensure accuracy and alignment with Regulatory requirements.
Implement Change Control Processes:
- Develop robust change control processes for labeling updates and tracking any modifications to core documents promptly.
- Ensure that changes are implemented consistently across global and regional labels.
Monitor Compliance:
- Establish mechanisms for ongoing monitoring of compliance with evolving Regulatory standards.
- Stay informed about changes in regulations and update labeling documents accordingly.
Utilize Technology and Automation:
- Leverage Regulatory labeling software and technology to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and document management.
- Explore tools that support artificial intelligence to streamline data sheet implementation and review processes.
Engage Regulatory Experts:
- Engage Regulatory experts or consultants within your organization or through your chosen service provider to provide insights and guidance throughout the labeling process.
Continuous Improvement:
- Establish a culture of continuous improvement, regularly reviewing and refining labeling processes based on feedback, industry changes, and evolving Regulatory landscapes.
Can Regulatory Labeling Services Assist in Post-market Monitoring?
Yes, Regulatory labeling services can indeed assist in post-market monitoring for pharmaceutical products. These services play a crucial role in supporting post-market surveillance by facilitating the management of labeling updates, handling safety-related labeling changes, and ensuring compliance with post-approval Regulatory requirements. By maintaining accurate and up-to-date labeling information, Regulatory labeling services help pharmaceutical companies respond to safety concerns and implement necessary changes timely to support ongoing Regulatory compliance and patient safety.
Furthermore, Regulatory labeling services can aid in the efficient dissemination of updated safety information to healthcare professionals and patients. In the event of new safety findings or changes in risk profiles for pharmaceutical products, Regulatory labeling experts can assist in swiftly updating labeling content to reflect the latest safety data and Regulatory requirements. This proactive approach to post-market monitoring and labeling updates supports the timely communication of important safety information to healthcare providers and patients, contributing to enhanced pharmacovigilance and patient care.
Overall, Regulatory labeling services provide valuable support in post-market monitoring by ensuring that pharmaceutical products maintain accurate and compliant labeling throughout their lifecycle. By leveraging the expertise of Regulatory professionals and efficient labeling management processes, companies can effectively address post-market safety considerations and Regulatory obligations, thereby contributing to the ongoing safety and effectiveness of their products in the market.
Why choose Freyr?
A decade of Regulatory labeling excellence
Over 180 global experts in labeling services
Specializes in creating and managing essential documents
Expertise in Investigational Brochures, Core Data Sheets, and Company Core Data Sheets
Committed to global compliance and precision
Utilizes AI (Artificial Intelligence) for efficient Regulatory navigation
Quick Facts
+
+
+
Frequently Asked Questions
Core Data Sheets (CDS) provide a consolidated summary of critical drug information, including indications, dosages, and safety profiles. They ensure consistent communication of essential details across global markets, facilitating Regulatory compliance and informed decision-making. CDS also serve as a reference for creating local product labels.
Investigational Brochures (IB) detail clinical trial data and drug development information for investigational use, while Company Core Data Sheets (CCDS) summarize key safety and efficacy data for global Regulatory purposes, guiding label content and updates. CCDS are used to create product-specific labels for market approval.
Artificial intelligence enhances Regulatory labeling by automating data analysis, improving accuracy in content creation, and expediting document reviews. AI tools streamline labeling processes and ensure consistency across diverse Regulatory requirements. They also help in predicting and addressing potential compliance issues.
Multilingual labeling ensures that pharmaceutical products are accessible to diverse patient populations, meeting regional Regulatory requirements and enhancing safety by providing clear, understandable instructions and warnings in multiple languages. This reduces the risk of miscommunication and errors in drug administration.
A centralized labeling management system coordinates the creation, review, and update of labeling documents, ensuring consistency and compliance across global markets. It streamlines processes and maintains accurate, up-to-date product information. This system also supports efficient handling of labeling changes and Regulatory updates.
Structured Product Labeling (SPL) is an XML-based format used for drug labeling that standardizes and organizes product information. It ensures consistency and facilitates easier data exchange between Regulatory agencies and manufacturers. SPL supports the efficient management of labeling information throughout a product's lifecycle.
Global Location Number (GLN) is a unique identifier used to identify locations and entities within the supply chain. It helps in tracking and managing pharmaceutical products accurately across global markets. GLNs ensure precise and efficient product distribution and inventory management.
The National Drug Code (NDC) is a unique identifier for drugs, assigned by the FDA. It helps in the precise identification of drug products and facilitates inventory management and tracking. The NDC is crucial for accurate drug dispensing and Regulatory reporting.
An Investigator's Brochure (IB) provides detailed information on an investigational drug's clinical and preclinical data. It is used to inform clinical trial investigators about the drug’s safety, efficacy, and dosage for study purposes. The IB also supports ethical and informed decision-making in clinical research.