Ninsho (medical device certification) is a third-party certification system in Japan wherein a Registered Certification Body (RCB), accredited by the Minister of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW), certifies designated highly controlled medical devices. It is applicable to Class II and a limited number of Class III devices that have an associated Japan Industrial Standard (JIS). A few Class II medical devices with no established certification criteria require approval under the Shonin program.
What are the other Device Registration Pathways in Japan?
In Japan, the Todokede and Shonin pathways are also used for medical device approvals in addition to Ninsho. Depending on the risk category of the device and the availability of predicates in Japan, the manufacturer must carefully plan their device submission.
What are the Prerequisites for the Ninsho Certification?
Manufacturers registering their devices through the Ninsho pathway must meticulously plan the submissions in terms of the following:
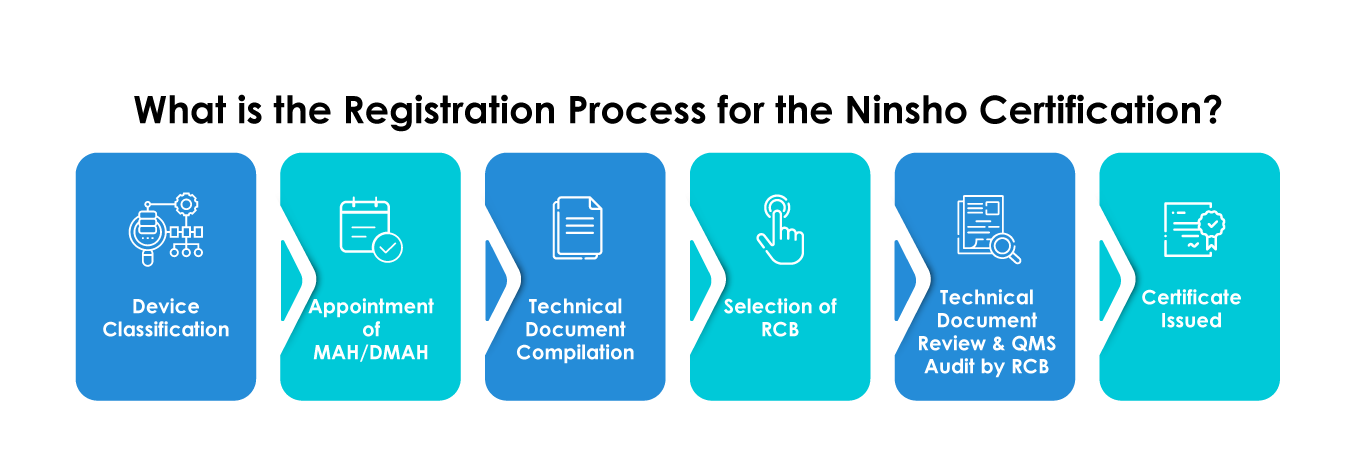
- Selection of an RCB
- Submitting general device data such as medical device category, intended use, efficacy risk analysis data, clinical data, etc
- Providing Summary of Technical Documentation (STED)
- Provision of documents should be in Japanese language only
- Foreign manufacturers must mandatorily appoint a Marketing Authorization Holder (MAH) or a Designated Marketing Authorization Holder (DMAH)
- Foreign manufacturers must register with MHLW and obtain a Foreign Manufacturer Registration (FMR) certificate for their manufacturing establishments
What are RCBs?
The Registered Certification Bodies (RCBs) are third-party certification bodies accredited by the MHLW. RCBs are responsible for reviewing and certifying medical devices eligible for and applied under the Ninsho pathway. RCBs are also responsible for carrying out the QMS audit of the manufacturer’s facility.
What are the QMS Requirements for Device Registration under the Ninsho Pathway?
Manufacturers must comply with all the QMS requirements defined under Ordinance 169. The MAH or DMAH must submit the application to the RCBs. The RCBs will carry out a detailed QMS inspection of the manufacturer's facility and, upon satisfactory implementation of the QMS, issue the certificate.
What is the Average Timeline Required for the Ninsho Certification?
The RCB typically requires three (03) to five (05) months to complete the technical evaluation, execute the QMS audit, and issue the Ninsho certificate.
Is there any Expiration Timeline for the Ninsho Certification?
Medical device registration doesn’t expire, but the sponsor should renew the QMS certificates every five (05) years.
Japan, being the third largest market for medical devices after the USA and China, offers great opportunities for medical device manufacturers worldwide. Manufacturers willing to market their devices in Japan must carefully plan the medical device certification and approval as PMDA has specific Regulatory requirements. Manufacturers can opt for a reliable Regulatory partner for hassle-free access to Japan market.
To find out more about medical device certification in Japan or any other PMDA Japan regulations, Contact Freyr Today!