
You've spent months developing your medical device software, hiring the best engineering talent, and creating what you believe is an innovative product. Then comes the Regulatory review, and you see that your IEC 62304 documentation is incomplete.
Sound familiar?
You're not alone, this situation plays out countless times across the medical device industry, costing companies months of delays and thousands of dollars in rework. What most of the medical device companies get wrong is that they treat IEC 62304 compliance as a documentation use rather than a complete safety framework.
The result?
Failed audits, Regulatory rejections, and compromised patient safety.
This blog will cover: What is IEC 62304? The software safety classifications it defines, and the path to compliance.
What is IEC 62304 and Why It Matters for Your Device?
IEC 62304 is an international standard for medical device software lifecycle processes, recognized by the US FDA and other Regulatory agencies worldwide. The standard isn't just another compliance checkbox – it's your roadmap to developing safe, effective medical device software that protects patients and gets to market faster.
The standard applies whenever software is an important component of medical device production, whether your software stands alone as a medical device (Software as a Medical Device or SaMD), is rooted within a device (Software in a Medical Device or SiMD), or is used in manufacturing. Think everything from mobile health apps to complex surgical robots. If your software falls under this umbrella, you need an IEC 62304 certification.
Why does IEC 62304 Compliance matter?
- Required for FDA clearance and CE marking for SaMDs
- Systematic approach to identifying and mitigating software-related risks
- Harmonized standard accepted globally
- Documented proof of due diligence in software development
- Faster time-to-market with proper planning
Our experience working with medical device companies globally has shown that organizations applying IEC 62304 early in their development process achieve first-time-right submissions and reduce time-to-market by an average of 4 to 6 months.
Understanding IEC 62304 Software Safety Classifications
IEC 62304 compliance begins with correctly classifying your software's safety risk. If you get this wrong, you'll either overengineer your documentation or miss critical safety requirements.
IEC 62304 Class A: No Injury Possible
- No contribution to hazardous situations
- Minimal documentation requirements
- No unit verification required
- Example: Administrative software for scheduling appointments
IEC 62304 Class B: Non-Serious Injury Possible
- Can contribute to hazardous situations resulting in non-serious injury
- Moderate documentation and testing requirements
- Unit verification required
- Example: Software that monitors vital signs but has backup systems
IEC 62304 Class C: Death or Serious Injury Possible
- Can contribute to hazardous situations resulting in death or serious injury
- Highest level of documentation and verification is required
- Detailed design documentation is mandatory
- Example: Software controlling insulin delivery or life support systems
Risk Classification isn't just about what your software is intended for – it's about what happens when it fails. A simple app that provides dosage calculations could be Class C if incorrect calculations could lead to serious harm.
5 Essential IEC 62304 Processes You Must Implement:
IEC 62304 establishes requirements into five core processes (Clauses 5-9) along with the step-by-step implementation guide.
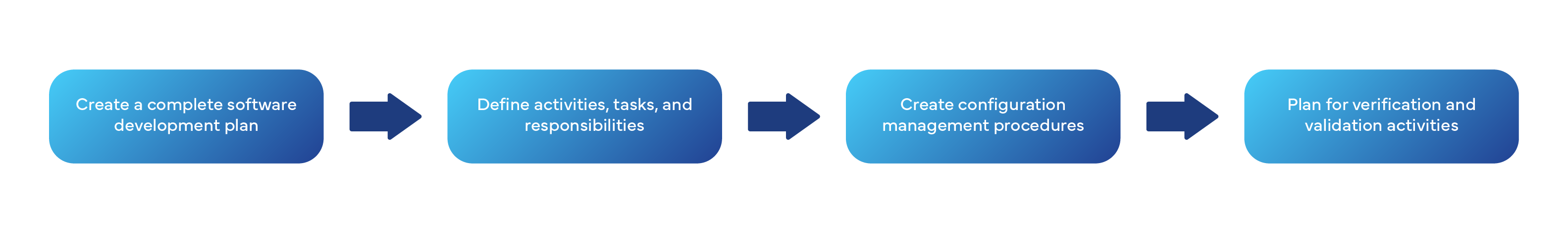
Process 1: Software Development Planning (Clause 5.1)
What must you do??
Process 2: Software Requirements Analysis (Clause 5.2)
What must you do??
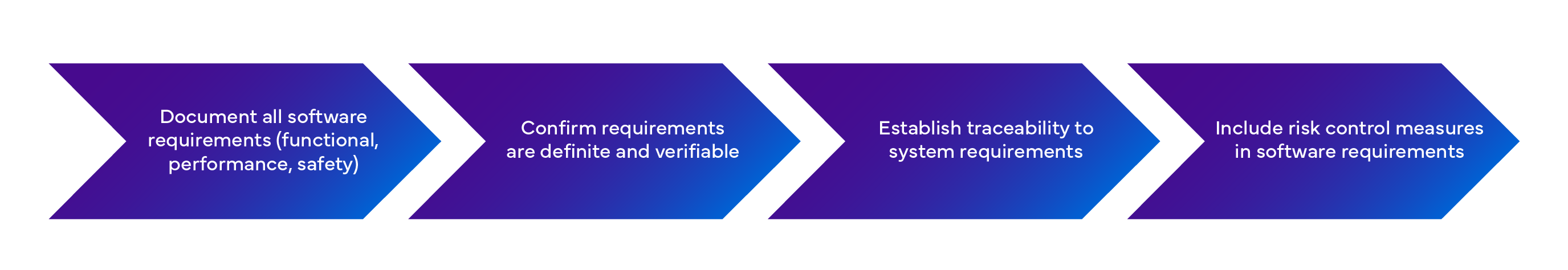
Pro tip: Supplies that can't be tested aren't requirements – they're wishes. Every requirement must have a corresponding verification method.
Process 3: Software Architecture and Design (Clauses 5.3-5.4)
Key deliverables:
- Software architectural design
- Meticulous design for Class C software
- Interface specifications
- Segregation strategy for risk control
Architecture reality check: Can you explain your software architecture to a regulator in 10 minutes? If not, it's too complex or poorly documented.
Process 4: Implementation and Testing (Clauses 5.5-5.7)
Required testing levels:
- Unit testing (Class B and C)
- Integration testing (Class B and C)
- System testing (all classes)
- Acceptance testing
Testing truth: More testing doesn't equal better testing. Should emphasize risk-based testing that validates your safety requirements.
Process 5: Risk Management Integration (Clause 7)
This is where many companies make mistakes. IEC 62304 risk management isn't a separate activity – it's integrated throughout your development process.
Software risk management requirements:
- Find out how software adds to hazardous situations
- Define risk control measures for each potential cause
- Confirm the effectiveness of risk control measures
- Maintain traceability from hazards to controls
Navigating SOUP: Software of Unknown Provenance in IEC 62304
Every medical device software system uses third-party components – operating systems, databases, libraries, and cloud services. IEC 62304 calls these "Software of Unknown Provenance" (SOUP), and working them properly is critical for compliance (eg, Windows, Linux, Android, MySQL, TCP/IP stacks, AWS, Azure, Google Cloud APIs, Cryptography, image processing).
SOUP identification requirements:
- Document name, version, and manufacturer of each SOUP item
- Explore potential risks to patients, operators, and third parties
- Assess published anomaly lists like bugs
- Validate why each SOUP item is suitable for its intended use
SOUP risk management strategy:
- Cover SOUP failures to prevent system-wide impacts
- Implement watchdogs and health checks
- Provide backup functionality for critical SOUP
- Validate SOUP behavior in your specific use case
IEC 62304 and ISO 14971: Making Risk Management Work Together
IEC 62304 doesn't replace ISO 14971 risk management – it extends it for software-specific risks.
Integration approach:
Start with ISO 14971 and conduct system-level hazard analysis
- Identify software causes for each hazardous situation, decide if software could be a contributing cause
- Apply IEC 62304 by documenting software-specific risk control measures
- Verify effectiveness by testing that your software controls actually work
ISO 14971 studies the probability of harm; IEC 62304 assumes 100% failure probability and focuses on consequences.
Common IEC 62304 Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Pitfall 1: Misclassifying Software Safety Class
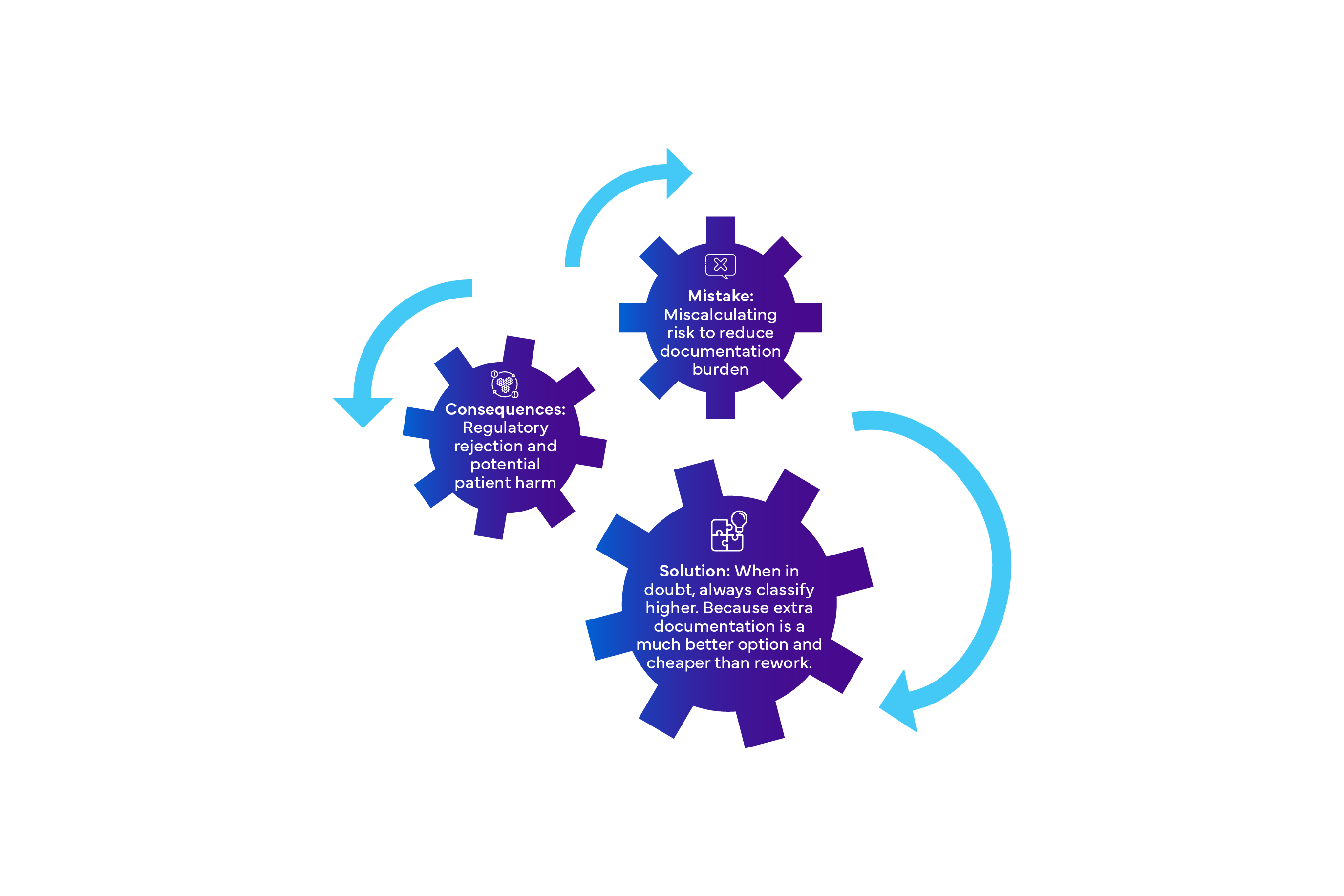
Pitfall 2: Inadequate SOUP Management
- Mistake: Giving third-party software as "someone else's problem"
- Consequence: Uncontrolled risks and compliance failures
- Solution: Maintain a complete SOUP inventory with risk assessments
Pitfall 3: Poor Integration with Quality Management System
- Mistake: Treating IEC 62304 as a standalone standard
- Consequence: Disconnected processes and audit findings
- Solution: Integrate IEC 62304 requirements into your ISO 13485 QMS
Pitfall 4: Insufficient Change Control
- Mistake: Informal software maintenance processes
- Consequence: Uncontrolled changes that introduce new risks
- Solution: Implement robust configuration management and problem resolution processes
Pitfall 5: Documentation Overload
- Mistake: Creating documentation that nobody uses
- Consequence: Audit failures and project delays
- Solution: Focus on meaningful documentation that supports decision-making
Your IEC 62304 Compliance Checklist
- Software safety classification assigned and documented
- Quality management system established (ISO 13485 aligned)
- Risk management processes defined (ISO 14971 aligned)
- Roles and responsibilities assigned
- Development plan created and maintained
- Software requirements documented and traceable
- Architecture designed and reviewed
- Detailed design completed (Class C)
- Unit verification performed (Class B/C)
- Integration testing completed (Class B/C)
- System testing performed (all classes)
- Software released with proper documentation
- Maintenance plan documented
- Problem resolution procedures established
- Change impact assessment process defined
- Post-market surveillance plan implemented
- Configuration items identified
- Version control system implemented
- Change control procedures established
- Configuration audits scheduled
- Software hazard analysis completed
- Risk control measures implemented
- Verification of risk controls performed
- Traceability matrix maintained
Best Practices for Ongoing IEC 62304 Compliance
- Begin IEC 62304 events during project planning, not at the end of development. Late-stage compliance efforts are expensive and often inadequate.
- Use tools for configuration management, testing, and documentation generation. Manual processes don't scale and introduce errors.
- IEC 62304 compliance isn't just for quality engineers. Developers, testers, and project managers all need to understand their roles.
- Software doesn't end at release. Plan for ongoing maintenance, updates, and cybersecurity patches from day one.
- Conduct internal audits to identify gaps before external assessments. Prevention is cheaper than remediation.
How Freyr Can Accelerate Your IEC 62304 Journey
Freyr accelerates medical device market entry.
With 2,200+ Regulatory experts and a track record of 1,500+ device approvals, we achieve a 99% first-time-right submission rate.
Specifically for IEC 62304, Freyr provides complete compliance services. Our proven methodology covers gap analysis, documentation, and lifecycle management to streamline conformity and get your device to market faster. Explore our IEC 62304 services here or reach out to us at sales@freyrsolutions.com.









