
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Good Distribution Practices (GDP) audits are critical for ensuring the quality, safety, and integrity of pharmaceutical products throughout their lifecycle. Conducting thorough investigations during these audits is essential to identify and rectify any deviations, non-compliance issues, or potential risks. In this blog post, we'll explore the importance of in-depth investigations during GMP/GDP audits and provide valuable insights into conducting effective investigations for regulatory compliance.
Understanding the Importance of In-Depth Investigations
- Identify Root Causes: In-depth investigations help uncover the underlying causes of deviations or non-compliance issues, allowing companies to address the root causes rather than just treating the symptoms.
- Prevent Recurrence: By understanding the root causes, companies can implement corrective and preventive actions (CAPAs) to prevent similar issues from recurring in the future, thus improving overall compliance and product quality.
- Ensure Product Safety: Thorough investigations ensure that any potential risks to product safety or efficacy are promptly identified and mitigated, safeguarding patient health and well-being.
- Maintain Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory authorities expect companies to conduct thorough investigations into GMP/GDP deviations and take appropriate corrective actions to maintain compliance with regulatory standards.
Key Steps in Conducting In-depth Investigations:
- Document Review: Start by reviewing relevant documentation, including standard operating procedures (SOPs), batch records, deviation reports, and previous audit findings to gain insights into the issue at hand.
- Root Cause Analysis: Utilize tools and methodologies such as the 5 Whys, Fishbone (Ishikawa) diagrams, or Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to systematically identify the root causes of deviations or non-compliance issues.
Fishbone Diagram as an Example
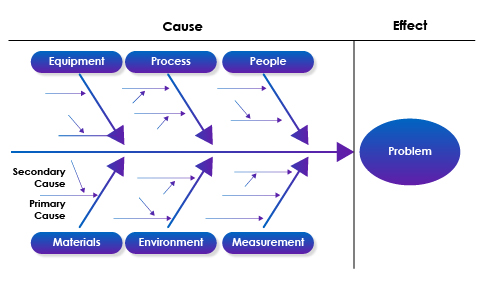
- Data Collection: Collect relevant data and evidence through interviews, observations, and data analysis to support the investigation findings and conclusions.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Involve cross-functional teams, including quality assurance, manufacturing, supply chain, and regulatory affairs, in the investigation process to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the issue and facilitate effective problem-solving.
- Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPAs): Develop and implement CAPAs based on the investigation findings to address the root causes and prevent recurrence of similar issues in the future.
- Continuous Improvement: Use the insights gained from investigations to drive continuous improvement initiatives, such as process optimization, training programs, or technology upgrades, to enhance overall quality and compliance.
Conclusion:
Conducting in-depth investigations during GMP/GDP audits is essential for maintaining compliance, ensuring product quality, and protecting patient safety. By following systematic investigation processes, identifying root causes, and implementing robust corrective and preventive actions, companies can strengthen their quality management systems and demonstrate their commitment to regulatory compliance and continuous improvement. Effective investigations not only mitigate risks but also contribute to building a culture of quality and excellence within the organization.









