Validation protocol is defined as a documented plan for testing a medical device to confirm that the production process used to manufacture the product meets the specific user, technical, and Regulatory requirements. This includes a review of process variables and operational limitations and the analysis of test results under actual use conditions.
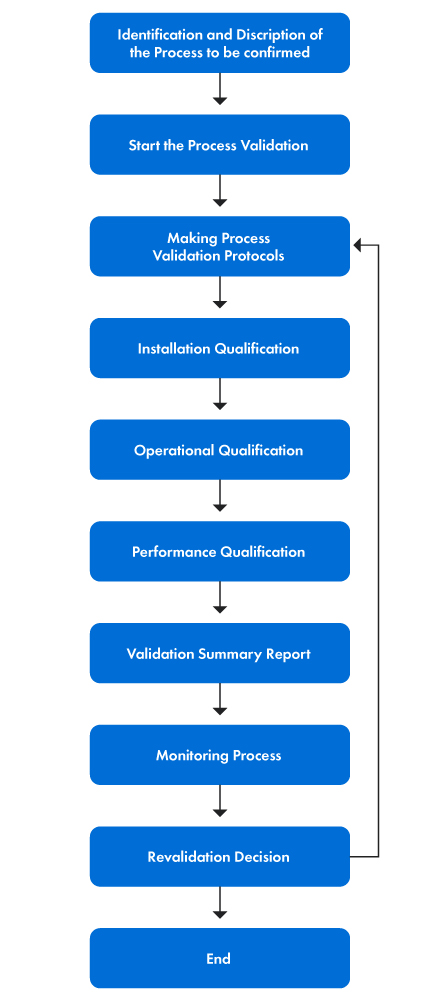
The validation process involves several tangible actions. The steps are elucidated as follows:
- First, the validation team is formed, and each member is assigned specific roles and responsibilities. The purpose of process validation is to provide a clear statement of the validation objectives and define the scope of the validation activities by specifying the aspects of the medical device that are being validated. The team then comprehends the underlying principles of the process to identify specific parameters and desired outcomes.
- Second, the evaluation and acceptance criteria are established, along with the selection of appropriate testing methods, tools, and statistical analysis techniques. Following this, process validation protocols are drafted, and the Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ), and Performance Qualification (PQ) are implemented.
- Last, ongoing process controls and monitoring measures are determined to ensure the continued validation of the process. Whenever necessary, revalidation is performed to maintain the accuracy and efficacy of the validation process.
Figure 1 below provides a step-by-step representation of the validation process.
Figure 1: The Stages of the Validation Process
PVP
Due to the wide range of production volumes and manufacturing complexities, there are numerous approaches to conducting process validation. However, the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) regulations and ISO 13485 provide limited suggestions on specific methods. Nevertheless, a widely recognized and authoritative source for medical device process validation is a guidance document from the Global Harmonization Task Force (GHTF), now called the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF), published in 2004. It remains the primary reference even on the USFDA’s official website.
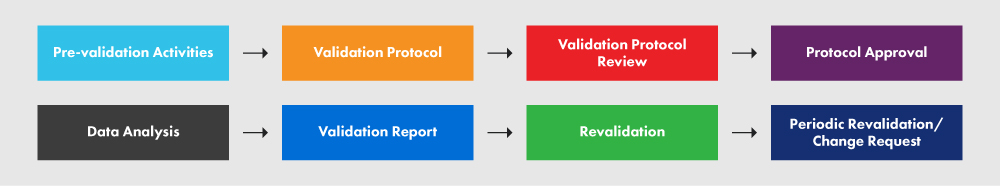
As per the guidance document, a validation team is formed to create a detailed Process Validation Plan (PVP). Process validation protocols include a detailed scheme on how to implement IQ, OQ, PQ, and revalidation. The PVP should contain the following elements:
- Defining the device and determining the validation approach.
- Identifying the elements that require validation.
- Conducting activities at the designated site.
- Outlining the scope of the documentation.
- Creating a schedule for the validation activities.
- Developing an overall master schedule.
- Maintaining a comprehensive list and references to both internal and external validations that have been performed.
The validation protocol is written before conducting validation activities. It should be prepared by the validation team and approved by the concerned department. The purpose of a validation protocol is to define the test scripts that must be followed to guarantee that the processes and equipment are ready to manufacture safe and effective medical device products.
An analytical report that contains information along with the necessary analysis, explanations, and recommendations, is part of the validation protocol. These records are further reviewed to ensure that the following two (02) criteria are met:
- Meeting of Regulatory standards.
- All records and data generated are reviewed for results, adequacy, and completeness.
Figure 2 below represents the PVP and the various processes involved in it.
Figure 2: The PVP and its Requirements
An appropriately drafted protocol provides clear guidelines, policies, and procedures to be adhered to during the process validation. It encompasses aspects such as facilities, equipment, methods, and training. The protocol specifies the process inputs and limits, as well as the essential steps for the successful execution of the process validation project. While the following outline does not encompass every single element required in your protocol, it does give you an overview of the level of detailing required. We strongly recommend following the guidance document for a better understanding of the process.
- Title Page
- Products to be Covered
- Equipment/Process to be Validated
- General
- Objectives
- Reference Documents
- Validation Plan
- IQ
- OQ
- PQ
- Measurement/Testing Equipment and Calibration
- Equipment Maintenance
- Revalidation
- Validation Team Approval/Signature Page
Operations management plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance by monitoring key measures, reviewing work methods and procedures, and taking prompt action when any issues arise. In cases where there are issues, you may need to revalidate a process partially or even fully. According to Section 820.75(c) of the USFDA Quality System Regulation (QSR), process revalidation should be considered under these circumstances: “When changes or process deviations occur, the manufacturer must review, evaluate, and perform revalidation as appropriate. These activities must be documented.”
Possible triggers for process revalidation include modifications to specifications, methods, procedures, software, designs, key components, batch scaling, location changes, equipment changes, and the like. Moreover, the implementation of Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) can also serve as a trigger for process revalidation. The primary reasons for revalidation are as follows:
- Changes made to the process.
- Negative trend in quality, sudden quality deterioration, or a spike in customer complaints.
- Major expansion of line capacity.
- Changes in design.
- Changes in product packaging.
- Transfer of a process to another facility.
- Changes in the application process.
To learn more about validation protocols and their importance in the field of medical device manufacturing, consult us Stay informed! Stay compliant!